Abundance: rare
What: young leaves, flower stalks, 1st year root
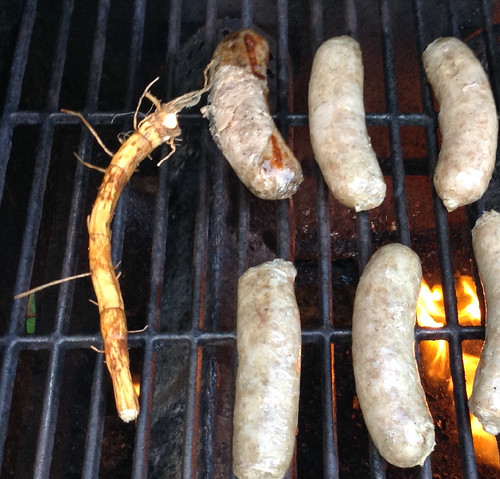
How: young leaves raw, as tea, stir-fried, or boiled in 2-3 changes of water; peel green skin of plant stalks to reveal inner white core which is eaten raw or cooked; root of 1st-year plants less than 1" in diameter and must be peeled then boiled in two changes of water until tender; roasted roots for coffee
Where: open fields, sunny areas, woods
When: leaves in spring, flower stalks in summer, roots summer and fall
Nutritional Value: Roots contain some minerals, vitamins C & B6, and some calories. Leaves contain many vitamins and phytochemicals
Other uses: you can stick a bunch of the burrs together to make a crown, but that usually ends badly
Dangers: burrs are clingy, do not confuse with toxic Cocklebur (Xanthium pennsylvanicum)
Medicinal Summary:
Root - liver protective and accelerator; anti-inflammatory (tisane, tincture)
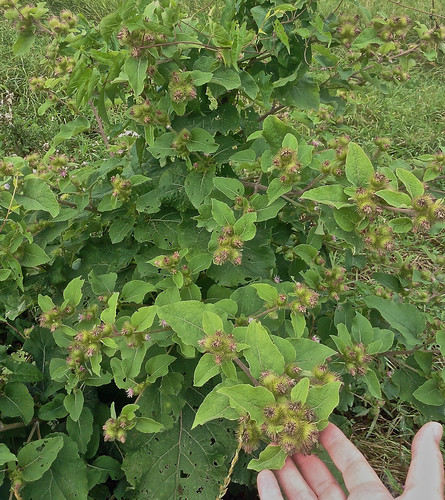
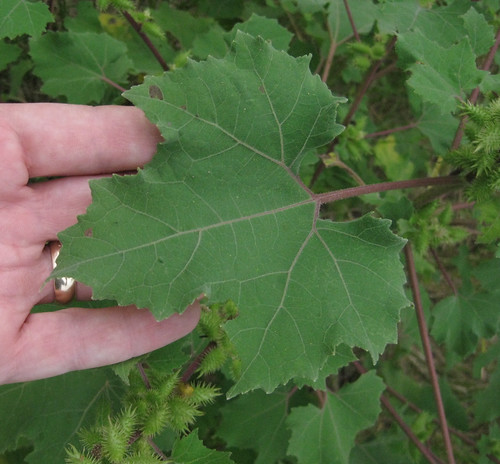
Burdock plant. Note the large, wavey-edged leaves.



Mature Burdock plant with flowers and immature seed bur. Leaves towards top of plant are much smaller than those at base.

Close-up of Burdock flower and seed bur.

Burdock stem.

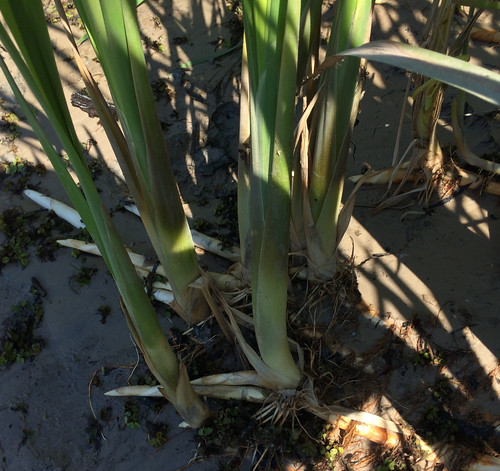
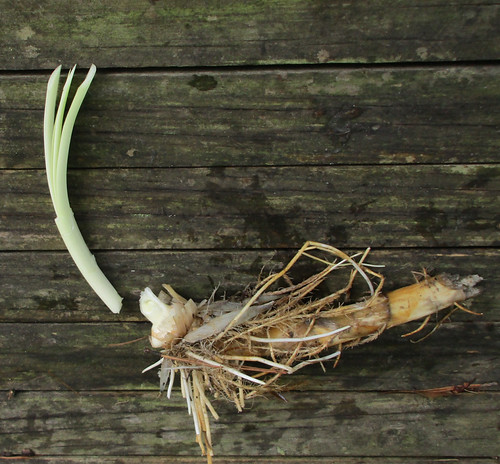
Burdock root (partial).

More burdock roots. These are up to 32 inches long.

Close-up of dried Burdock bur. Not the roundish shape and long, thin hooks.
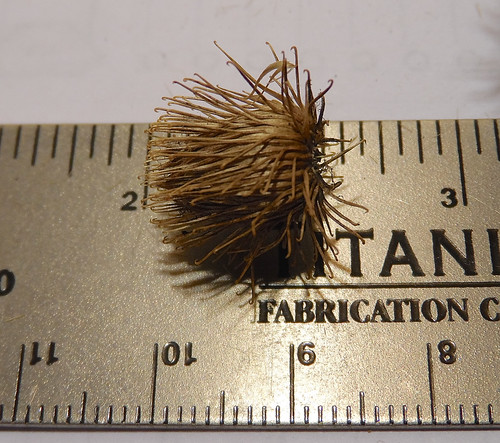

Close-up of cluster of Burdock burs.

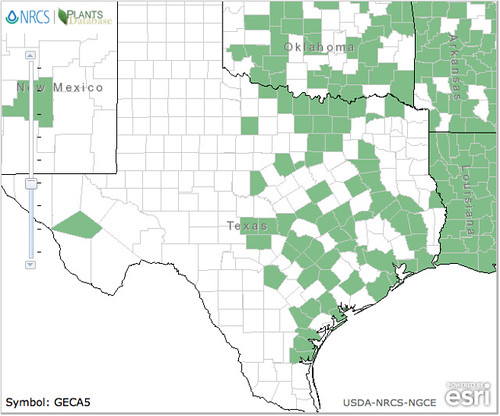
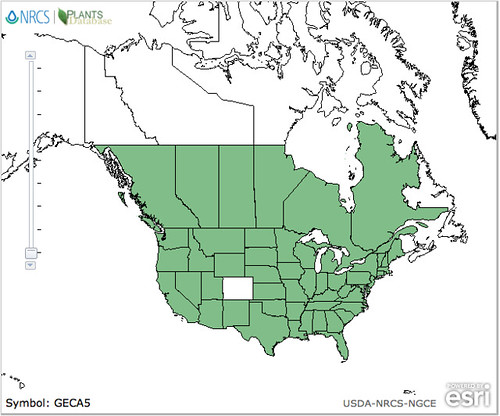
North American distribution, attributed to U. S. Department of Agriculture.
Burdocks prefer moist areas such as along stream banks and shady, wooded areas that stay wet. These biennial (live two years) plants produces large leaves the first year followed by flower stalks, flowers, smaller leaves, and clingy burs the second year. Both the Common Burdock (Arctium minus) and the Great Burdock (Arctium lappa) are edible. The outer rind of both the roots and plant stalks is very bitter and must be removed. If the root still has some bitterness boiling with changes of water will remove it. I find the peeled roots have a delicious sweet/savory flavor and a texture similar to bamboo shoots.
The peeled roots can also be used to make a caffeine-free coffee substitute. Dice the roots then roast them to your preferred level of darkness in an oven at 400F. Grind these roasted roots in a coffee grinder than either use as-is or mix with regular coffee grounds.
The roots are also excellent when pickled using the Ball Book of Canning recipe for pickling okra.
Cocklebur (Xanthium pennsylvanicum), which are toxic, also produce clingy burs. However, the burs of Cocklebur are much more oblong/cigar shaped than Burdock burs. Also, Cocklebur leaves are sharply toothed whereas the Burdock leaves have a wavy edge.
Cocklebur plant. Toxic, do not eat!

Close-up of the toxic Cocklebur leaf.

Buy my book! Outdoor Adventure Guides Foraging covers 70 of North America's tastiest and easy to find wild edibles shown with the same big pictures as here on the Foraging Texas website.