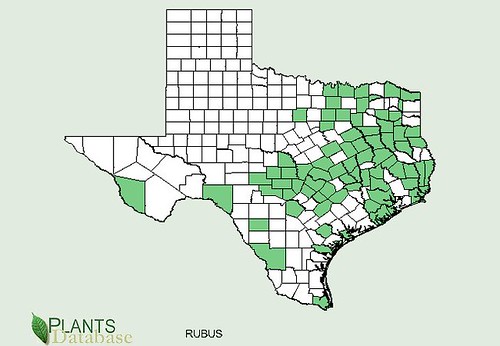
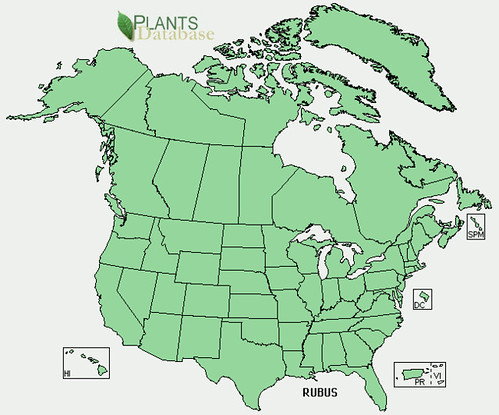
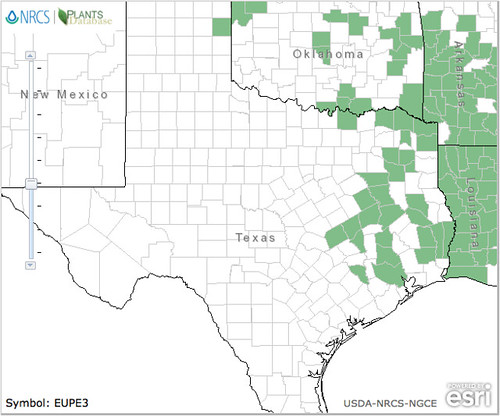
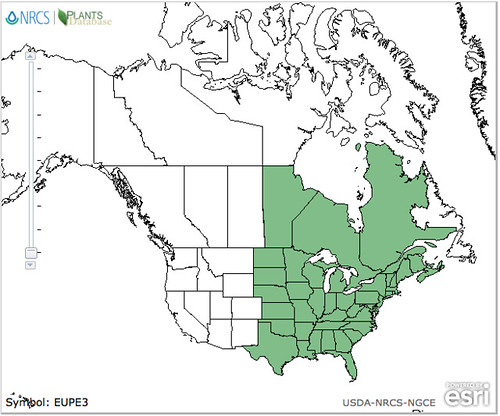
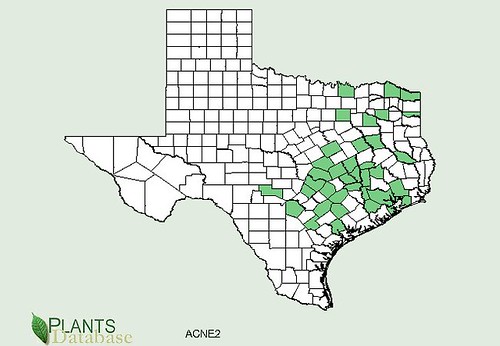
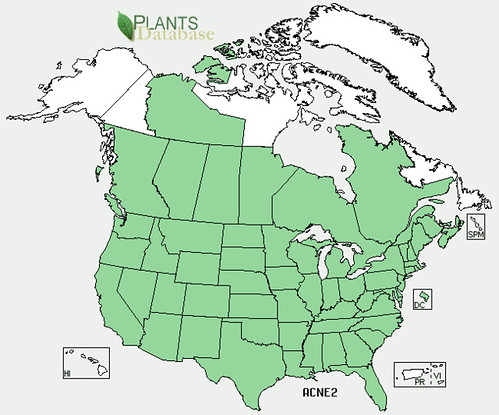
Abundance: invasive
What: leaves, flowers, seeds
How: raw, cooked, tea
Where: shade, woods, borders
When: summer
Nutritional Value: leaves have fiber, calcium, iron, potassium, vitamins A, C, riboflavin; seeds have omega-3 fatty acids
Dangers: dried plants can become toxic to cattle
Medicinal Summary:
Leaves - antiasthmatic, antibacterial, general antiseptic, antispasmodic, diaphoretic, emollient, expectorant, antioxidant; anti-inflammatory; antidepressant, and general tonic
Young Beefsteak Weed. The leave's flavor is excellent right now.

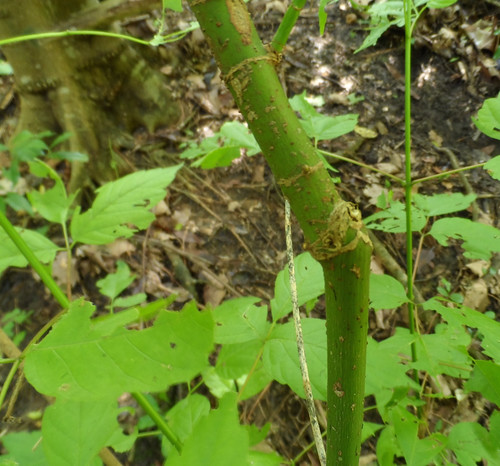
Mature Beefsteak plant.

Mature Beefsteak plant...note the purplish color on the underside of the leaf.

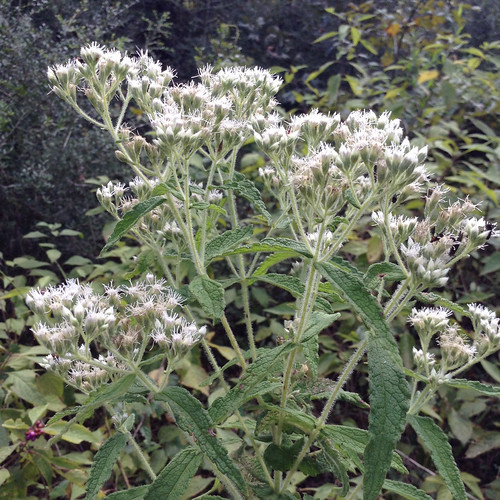
A stand of Beefsteak plants.

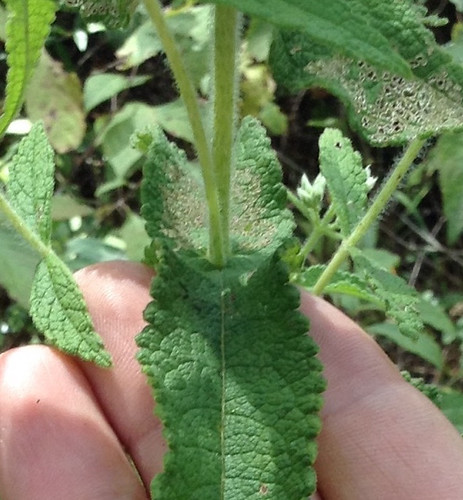
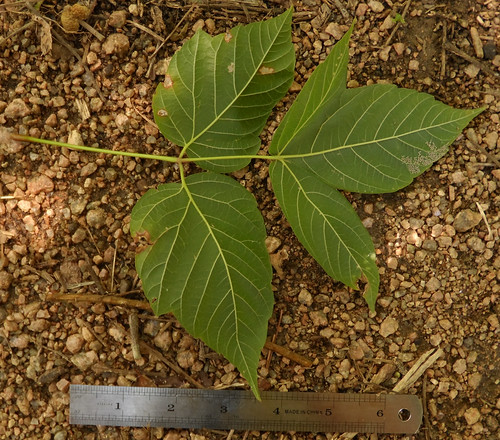
Close-up of leaf. Note the sharp teeth along the edge and how the veins run along the bottom of these teeth.

Close-ups of the reddish, hairy stem. Note the square shape, opposite leaves and how the flower stalks join the stems at the leaf joints.


Close-up of flower stalk after losing flowers. Note the alternating, opposite arrangement.

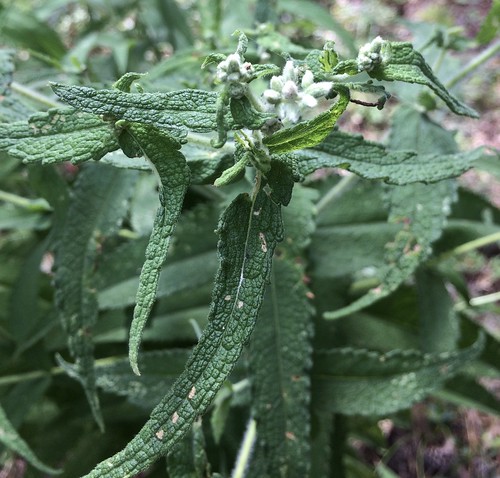
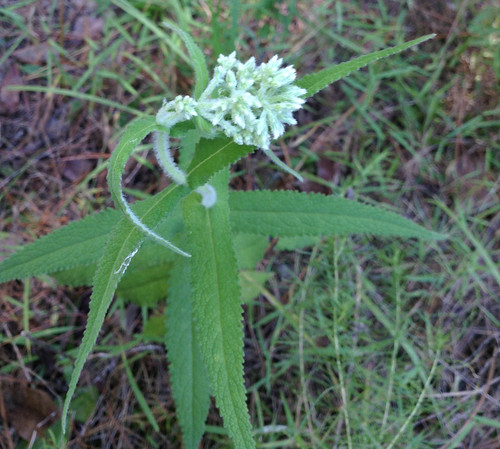
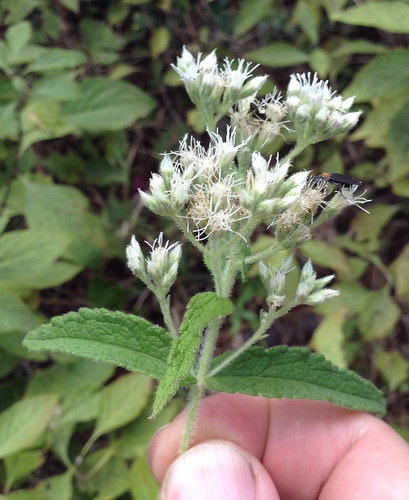
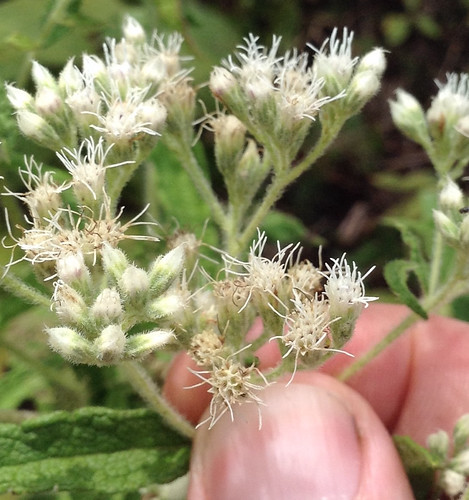
Close-up of flower.

North American distribution, attributed to U. S. Department of Agriculture.

Originally a popular seasoning herb and medicine in Asia, Beefsteak Weed has become an invasive plant across central and eastern United States. In Texas these plants are usually found near urban and suburban areas where they've gone feral from landscaping beds and gardens. Beefsteak plants seem to prefer disturbed areas, especially shady areas with moist but well-drained soil. Being in the mint family, Beefsteak Weeds have a strong minty scent, show the characteristic square hollow stem, have alternating-opposite leaves, and reproduce vigorously.
The sweetish-flavored young leaves have a long history of both being used in salads or cooked as a seasoning for rice and other dishes. The flower stalks (inflorescence) are used as garnishes. The seeds are roasted and mixed in with other dishes, dried and then ground as a seasoning, and were pressed for their oil. This oil is comparable to rapeseed oil.
An oil distilled from the leaves was used as a flavoring agent in both toothpastes and candy though these have been replaced by synthetic version nowadays.
The entire plant is dried then reconstituted in tea for medicinal uses. Traditional Asian herbal medicine states it is an antiasthmatic, antibacterial, general antiseptic, antispasmodic, diaphoretic, emollient, expectorant, and general tonic. It supposedly has strong anti-cancer properties.
Being invasive, it should be destroyed on sight but at least it can be used after harvesting. Maybe someday if enough people start eating it we can stop it from damaging native ecosystems.
Buy my book! Outdoor Adventure Guides Foraging covers 70 of North America's tastiest and easy to find wild edibles shown with the same big pictures as here on the Foraging Texas website.