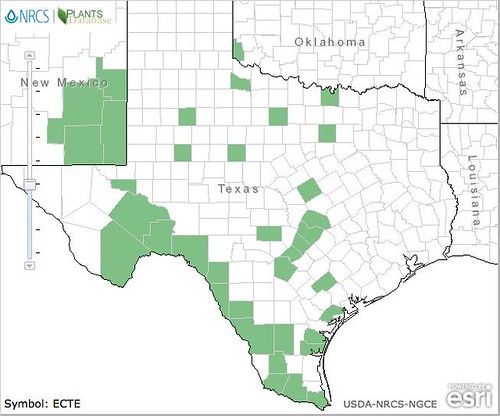
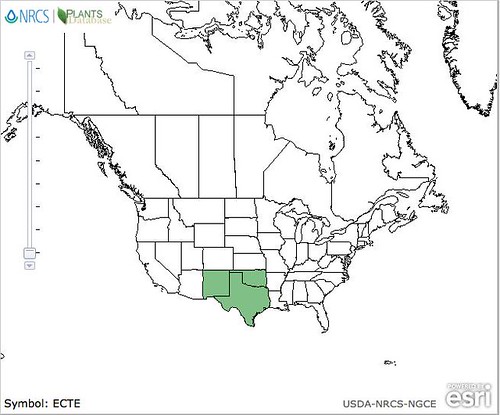
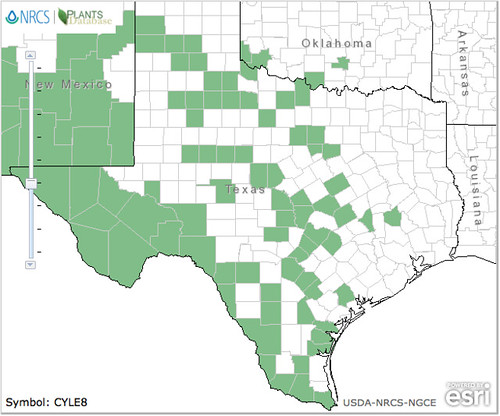
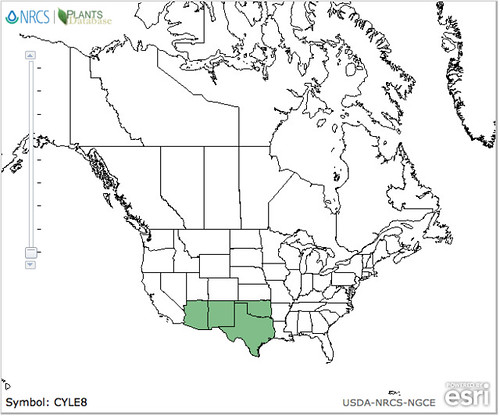
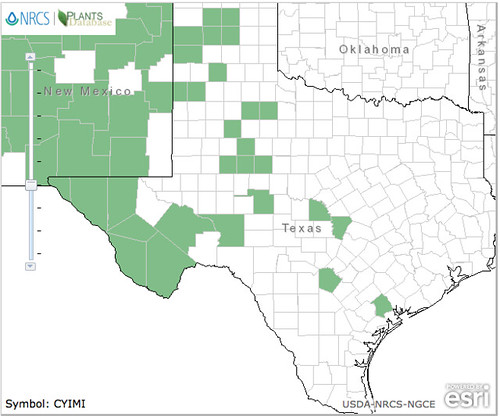
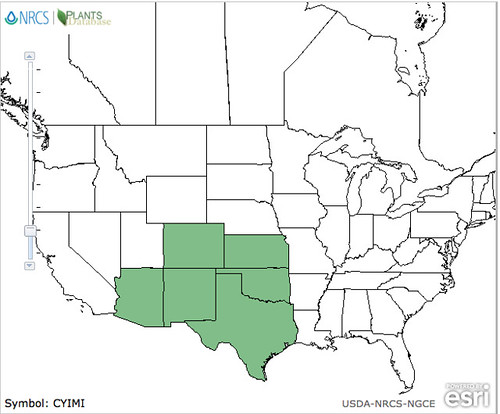
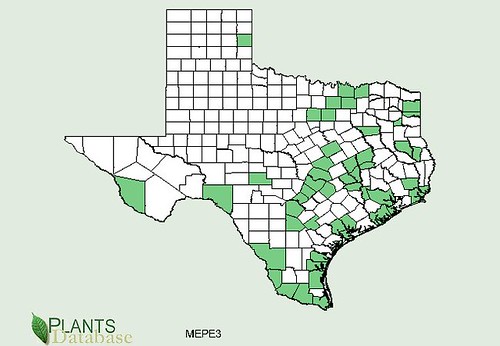
Abundance: rare
What: young leaves, stem, roots, seeds
How: leaves-raw/cooked; stem and roots-peel then boil; seeds-dry then add to soups and stews
Where: shade, borders, woods, marsh
When: spring, summer, fall
Nutritional Value: sugars/calories in stem and roots
Dangers: WARNING: Similar-looking to deadly, foul-smelling hemlock! Also, juice and hairs of cow parsnip can irritate skin and contains suspected cancer-causing chemicals.
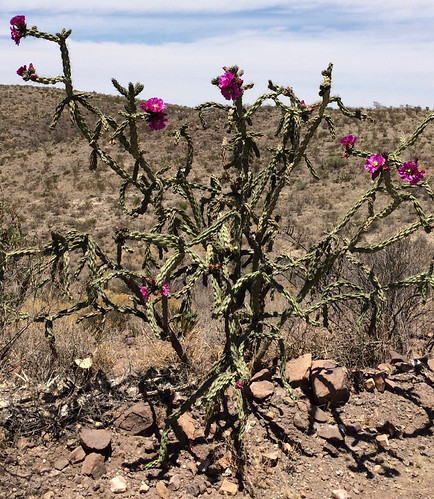
Cow parsnip plant (almost seven feet tall).

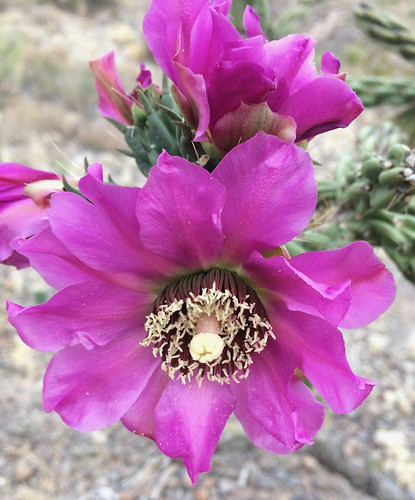
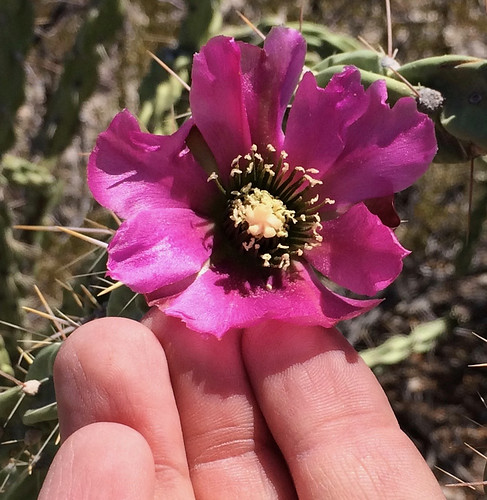
Closeup of flowers.

Another view of flowers.

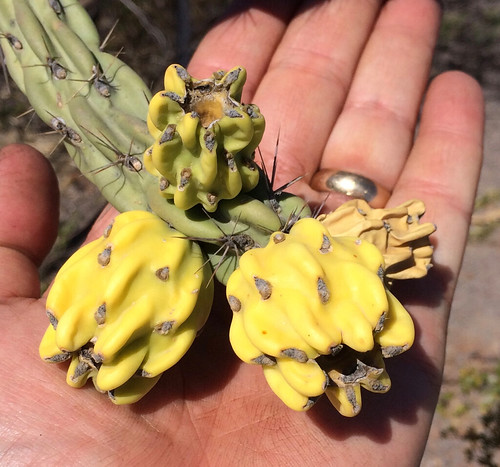
Mature seedhead of cow Parsnip.
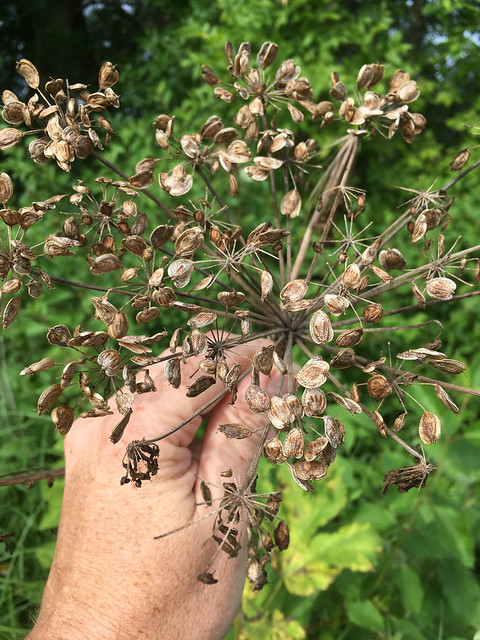

Leaves of cow parsnips are huge, well over twelve inches across.

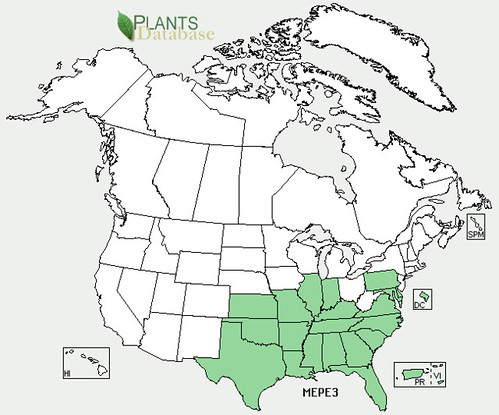
North American distribution, attributed to U. S. Department of Agriculture.
Look for Cow Parsnips in partially shady areas where water (usually a stream) meets woods. They seem to prefer hardwood forests to pine.
While not quite on par with Pokeweed, Cow Parsnips do require caution when harvesting and preparing the young shoots. Like Pokeweed, harvest the shoots when they're under 9" tall but you'll also want to take the cow parsnip's root. Wear gloves and arm guards while collecting them so the furanocoumarin chemical in the sap and surface needles can't adhere to your skin. If this chemical does get on you it'll make those areas of skin super-sensitive to sunlight, resulting in patches of 2nd degree sunburns.
Still the plant is quite tasty. Saute the diced-up leaves, stem, and roots in butter, oil, or bacon grease along with onions or garlic for a few minutes. They'll shrink a little but not disappearing like spinach. Hit them with a dash of cedar-infused apple cider vinegar and have at them!
Buy my book! Outdoor Adventure Guides Foraging covers 70 of North America's tastiest and easy to find wild edibles shown with the same big pictures as here on the Foraging Texas website.