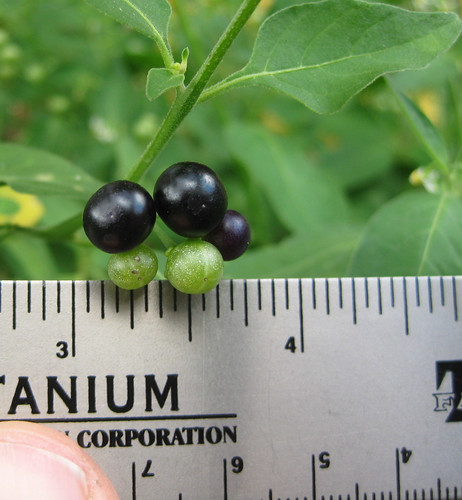
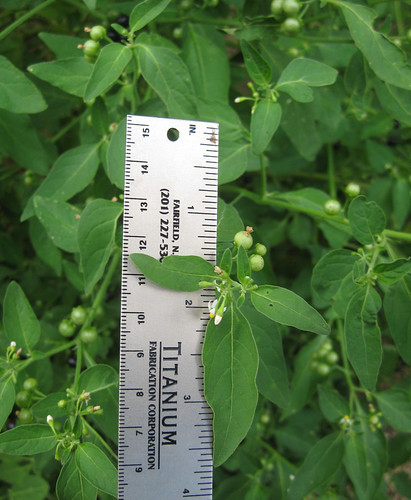
Abundance: common
What: young leaves, seeds
How: Young leaves raw or cooked, seeds eaten raw, roasted or ground into flour
Where: sunny fields, disturbed areas
When: summer
Nutritional Value: Grains supply protein, calories, and minerals. Leaves vitamins A & C along with minerals calcium, iron, and phosphorous, and also fiber.
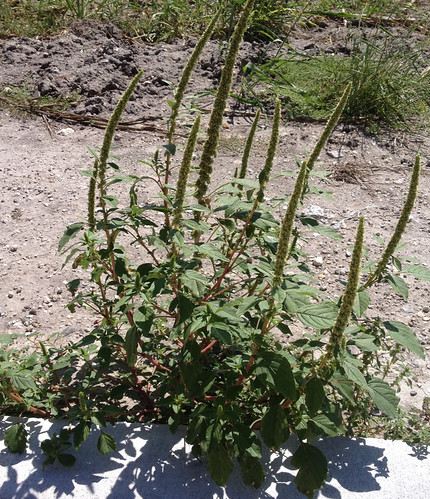

Another type of amaranth.

Another variation of amaranth.


Red amaranth (often used as decorative plant).
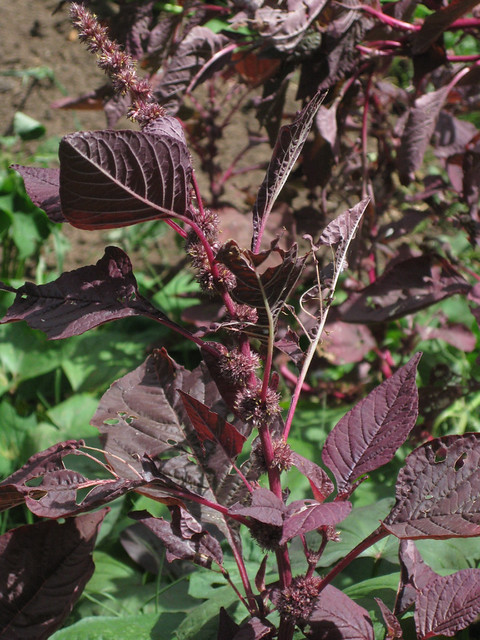

Another amaranth.


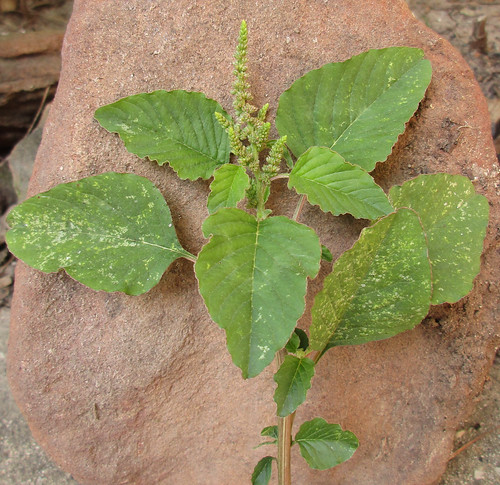
Still more amaranths.
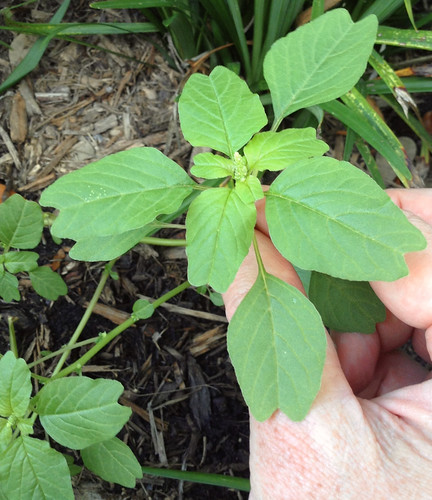
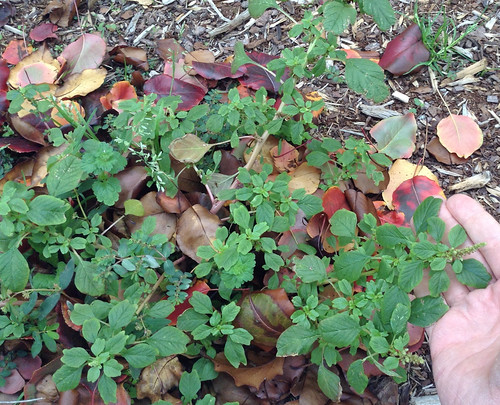


And yet more amaranths.


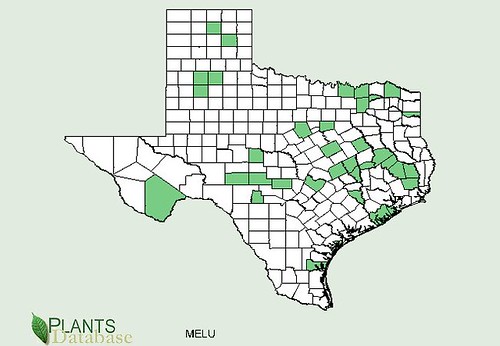
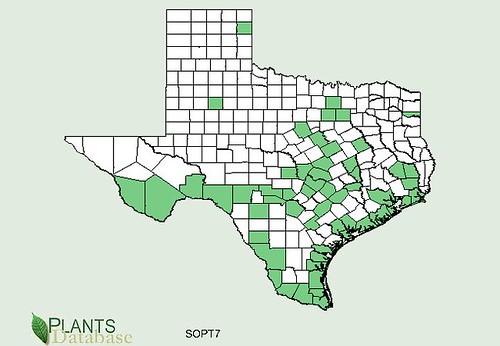
Texas distribution, attributed to U. S. Department of Agriculture. The marked counties are guidelines only. Plants may appear in other counties, especially if used in landscaping.

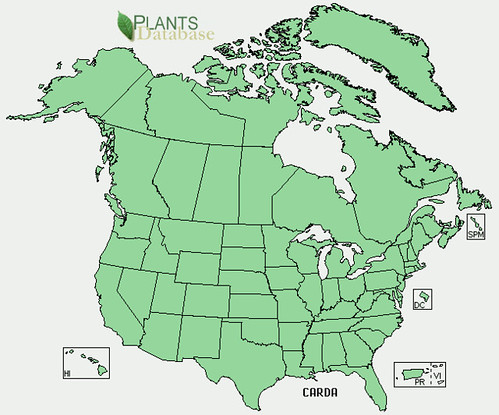
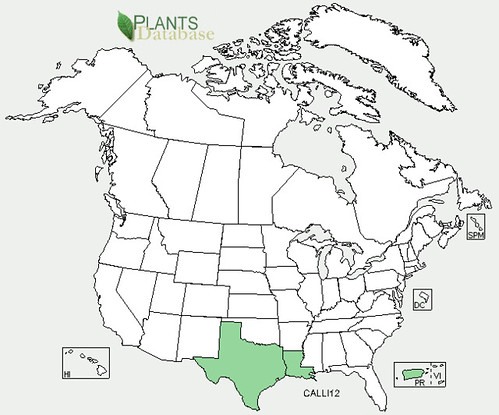
North American distribution, attributed to U. S. Department of Agriculture.
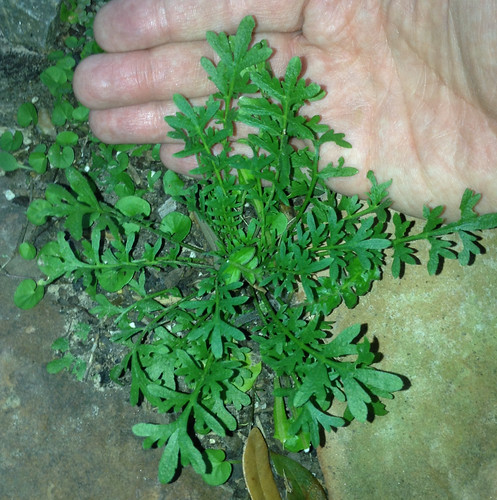
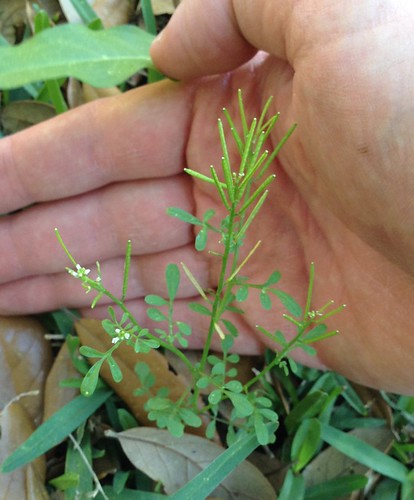
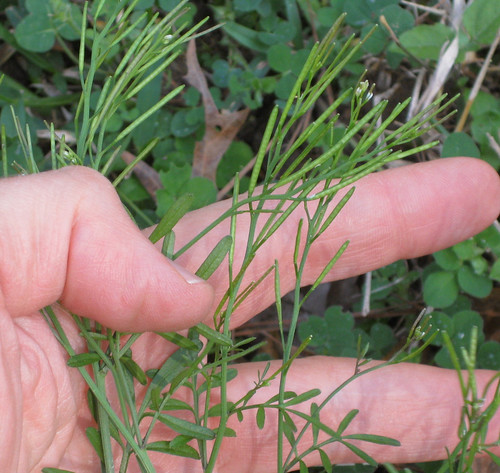
A variety of amaranth species can be found across Texas and the South. Shapes range from prostrate, creeping vine-like weeds to striking, tall, cultivated forms. The most distinctive feature of all amaranths is their spikes of tiny, clustered flowers which are the same color as the rest of the plant. Amaranths are most commonly found in sunny, disturbed areas and wastelands such as abandoned lots and roadsides. Bright red versions are often included in landscaping.
Amaranth leaves can be eaten raw or used as a spinach substitute in any dish. The leaves are high in vitamin A & C, assorted necessary minerals and also fiber. The youngest leaves have the best flavor and texture, but even the large, old leaves can be chopped up and included in any food needing a vegetable.
Amaranth seeds are very rich in carbohydrates and up to 16% protein by weight. Better still, the seeds contain the amino acid lysine which is very rare for plants but vital for human health. A single plant can produce as many as 100,000 of these wonderful, slightly nutty-tasting seeds. They can be eaten raw but toasting and then grinding into flour releases the most nutrition. The ornamental varieties are just as productive as the wild one but are more attractive. Amaranth seeds have even been used to make a gluten-free beer.
Buy my book! Outdoor Adventure Guides Foraging covers 70 of North America's tastiest and easy to find wild edibles shown with the same big pictures as here on the Foraging Texas website.