Abundance: common
What: flowers, leaves, bark
How: tea, poultice, tincture
Where: stream banks, arroyos of the desert areas
When: spring, summer
Nutritional Value: low
Dangers: don't mistake a poisonous, landscaping Oleander for desert willow!
Medicinal Summary:
Flower - tea soothes coughs
Bark & Root - teas and tinctures are antimicrobial and antifungal
Desert Willow in March in a gully in Big Bend Ranch State Park (no foraging allowed).

Close-up of flower in March in Big Bend Ranch State Park. Note the unopened buds higher up the branch.
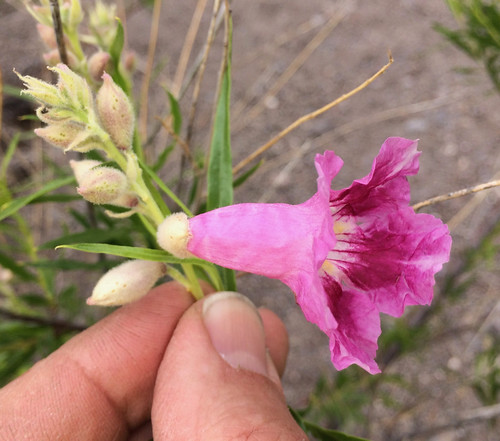

Another close-up of the flower.

Unopened flower buds in March in Big Bend Ranch State Park (no foraging allowed).

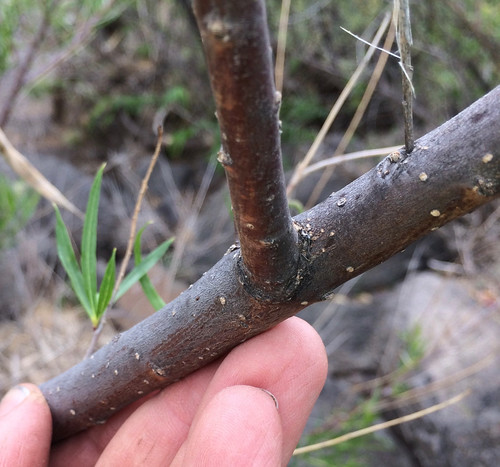
Desert willow bark is generally smooth, dark and spotted. Note the

Last year's dried seedpods may still be hanging on the desert willow. They have fluffy seed "parachutes" like milkweed.

Another desert willow growing along a dry streamback in Big Bend Ranch State Park (no foraging allowed).

Texas distribution, attributed to U. S. Department of Agriculture. The marked counties are guidelines only. Plants may appear in other counties, especially if used in landscaping.

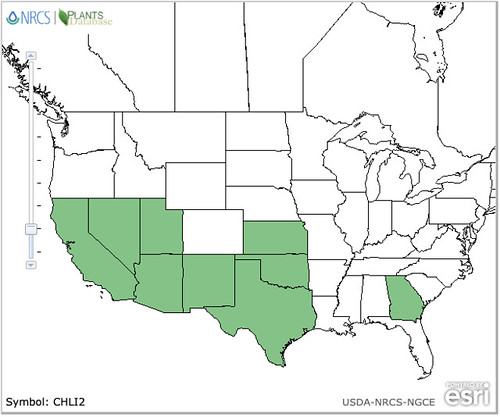
North American distribution, attributed to U. S. Department of Agriculture.
Late winter/early spring is a beautiful time in west Texas desert areas, especially along the streambeds that winter rains had soaked the soil briefly but thoroughly. The water walks up the desert, covering it with a confetti of flowers. Perhaps the most beautiful are the big, pink-purple flowers of the desert willow. This small, usually multi-trunked tree can be found growing upwards from the safety of large boulders along the arroyos of west Texas but also in a few counties randomly spread across Texas. Because of its compact but interesting growth pattern and wonderful flowers it is used as a xeriscape landscaping tree in many Texas cities from Houston to Amarillo.
Though note a true willow, the desert willow gets its name from its liner to lanceolate, hairless leaves. These leaves have pinnate vein patterns with a main, center vein from which secondary veins branch outwards and upwards, reconnecting out towards the edge of the leaf.The edges of the leaves are entire, lacking any sort of serrations or lobes. Oddly, the leaves can be arranged along the branches in both alternating and opposite patterns. A tea (tisane) or tincture made from the leaves and bark is antimicrobial, especially against fungal infections. Rinsing out the cuts and scratches one gets when traveling through the desert are well cared for with a wash of the leaf/bark tea. A tincture will also clean out wounds but will sting.
The violet-scented flowers are triggered by the earliest warm rains of spring. They sprout near the ends of branches beyond the leaves. These branches continue to grow and produce new flower buds into the summer. Pink and purple flowers with light-colored throats seem to be the most common but even white flowers are possible. The inside surface of the petal(s) can often be striped with a much darker shade than the rest of the flower.
Tea made from the fragrant flowers of desert willow is what you're really after. Gently tug on a flower and if it comes off the tree easily add it to a jar until the container is half full. Fill it to the top with water (approximately 1 part flowers, 2 parts water) and let it soak in the sunlight for half a day. Strain out the flowers, add some ice to cool it down, and drink the drink of desert secrets. Medicinally, the flower tea soothes rough coughs.
After the flowers come long, green seedpods. By fall these pods can be 6"-10" long and soon split open to release their fluffy seeds to float away. The brown, dried pods remain on the tree, helping identify it when the flowers aren't present. Though these long beans look inviting when green, they are not considered edible.
While these small trees require little water their growth indicates water is likely close to the surface. Digging around them can often uncover a seep of murky but life-giving water. Be sure to purify it as you would any wild water, such as by boiling, filtering, or a chemical treatment.
Buy my book! Outdoor Adventure Guides Foraging covers 70 of North America's tastiest and easy to find wild edibles shown with the same big pictures as here on the Foraging Texas website.

