Abundance: common
What: fruit
How: raw, cooked
Where: dry, desert areas
When: late summer, fall
Nutritional Value: calories
Dangers: spines are sharp!
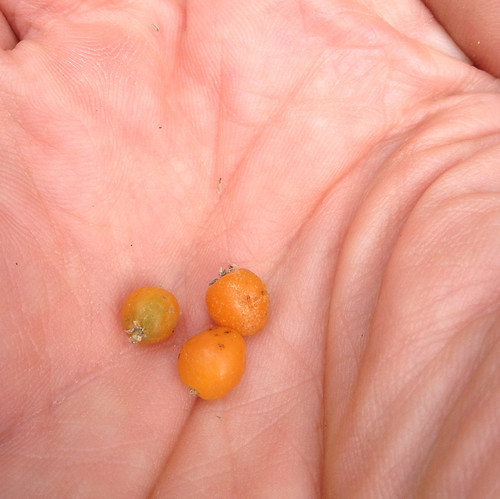
Desert Hackberry fruit when ripe.
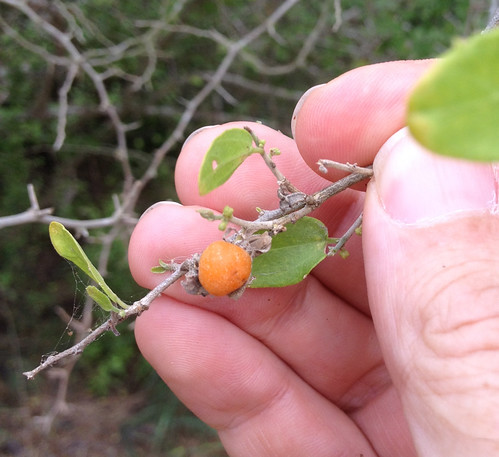

Close-up of ripe fruit.

Thicket of Desert Hackberry trees. They grow with interlaced trunks and branches.

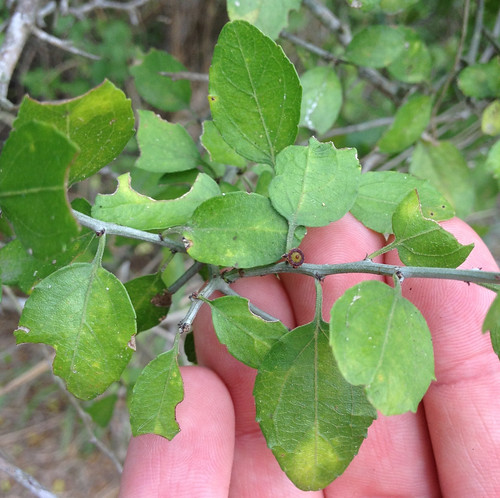
Close-up of leaves.

Note how the young branch "zig-zags" betweens leaf nodes and spines.

Close-up of spines on young twig.
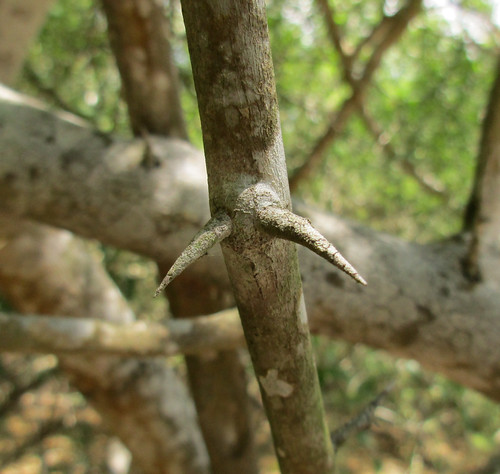

Close-up of spine on mature branch.

Desert Hackberry trunk.

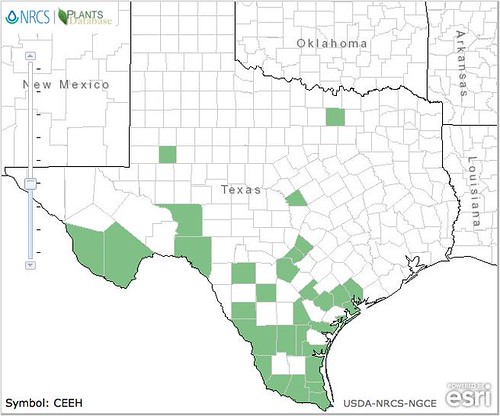
Texas distribution, attributed to U. S. Department of Agriculture. The marked counties are guidelines only. Plants may appear in other counties, especially if used in landscaping.
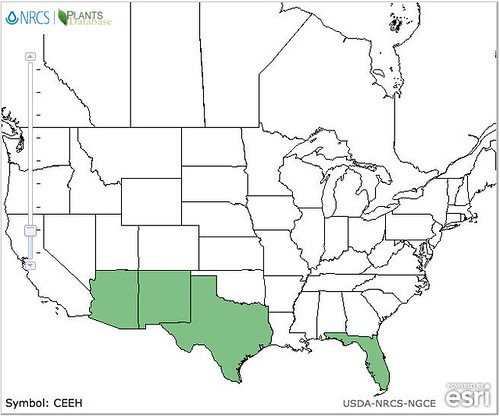
North American distribution, attributed to U. S. Department of Agriculture.
As much as I love Desert Hackberries, birds love them even more. The spiny thickets that these small tree form are are a safe, food-filled haven for all manner of small birds. Look for these thickets in arid, hot areas of south and west Texas, though in these environments they will likely cluster near water sources including dry gullies. The trees rarely get much over 15 feet tall. The small, oval leaves stay on the tree most of the year but can fall in extremely dry conditions.
The ripe fruit is quite sweet, orange in color, and its single seed is much softer than the hard stone found in Sugar Hackberry fruit. I eat the whole thing raw, seed and nut combined. It can be eaten raw, mashed then baked into a calorie-laden snack bar, or boiled in some water to make a syrup. A truly industrious person could gather enough of the ripe fruit to make a bottle of wine or two if they were willing to fight through the plant's thorns...and deal with the resulting angry birds.
Buy my book! Outdoor Adventure Guides Foraging covers 70 of North America's tastiest and easy to find wild edibles shown with the same big pictures as here on the Foraging Texas website.

