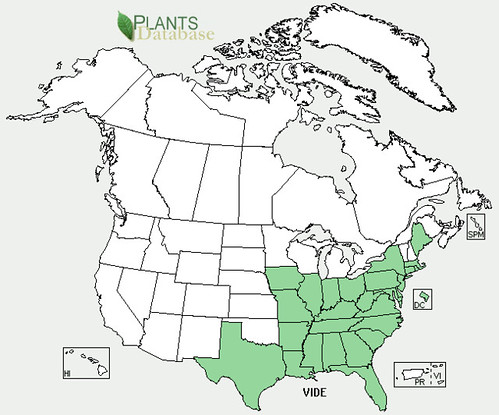
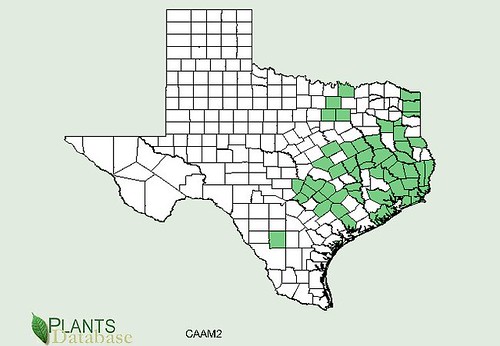
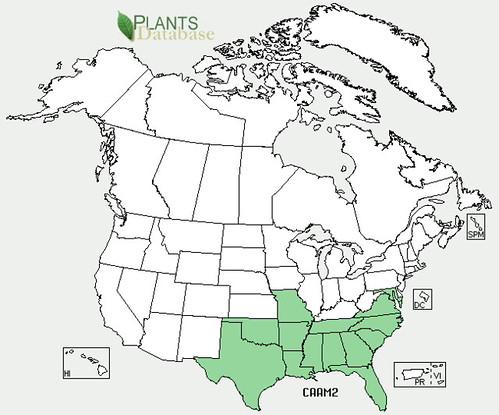
Abundance: rare
What: nuts
How: raw or roasted
Where: sandy, shaded areas near water
When: fall
Nutritional Value: calories, protein
Dangers: nut husks are very prickly
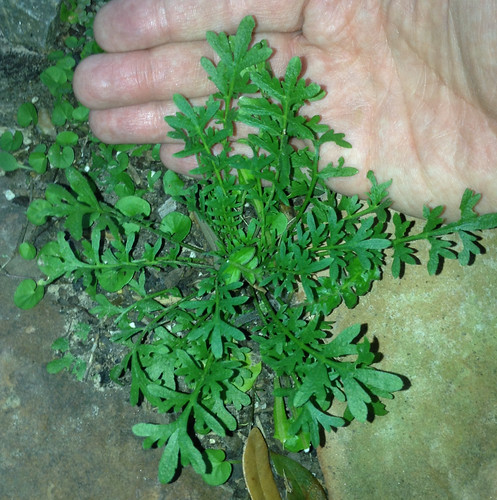
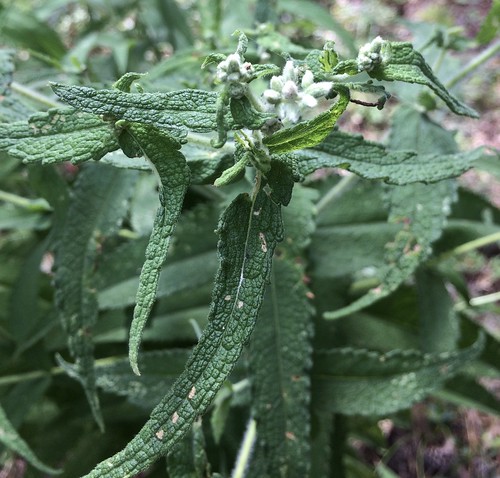
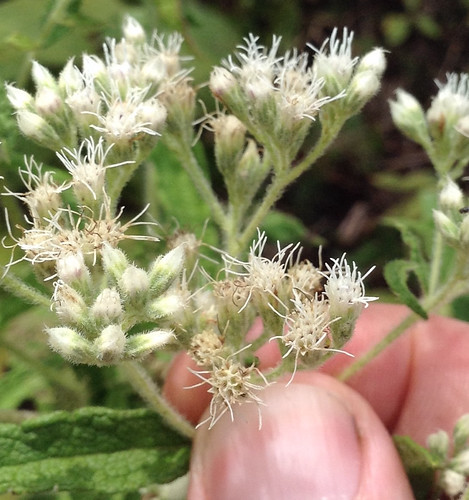
Allegheny Chinkapin leaves.

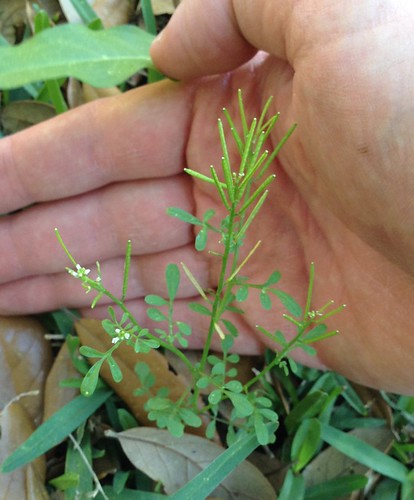
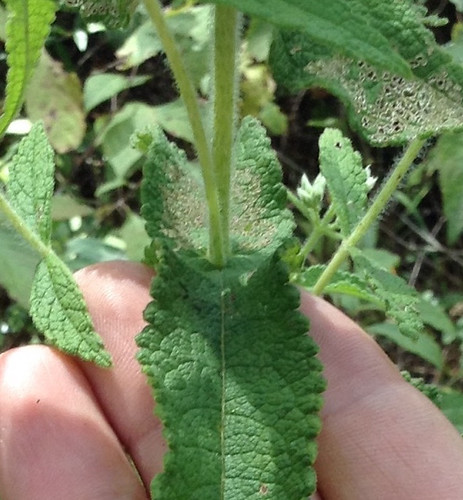
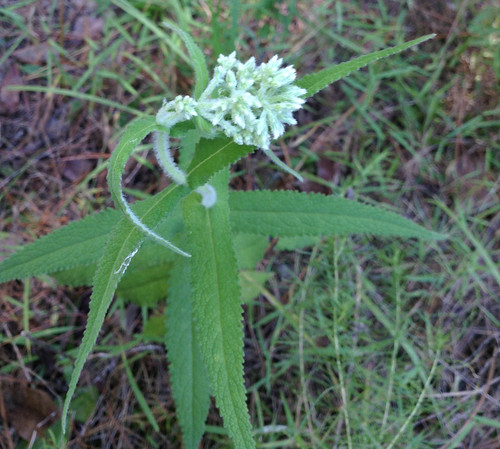
Close-up of leaves.

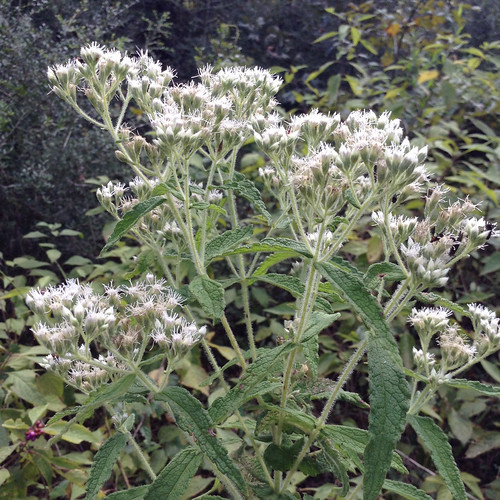
Nut pods in the fall, having dropped some of the nuts.
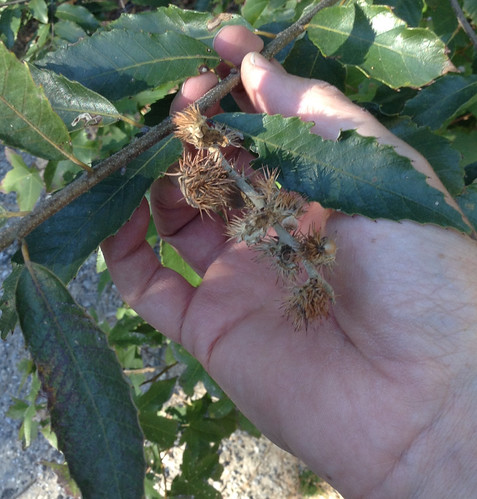

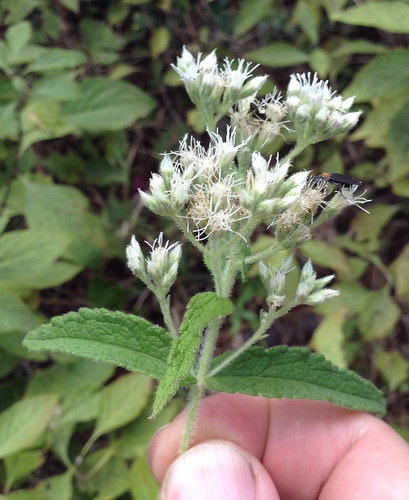
Close-up of pods with and without nuts.
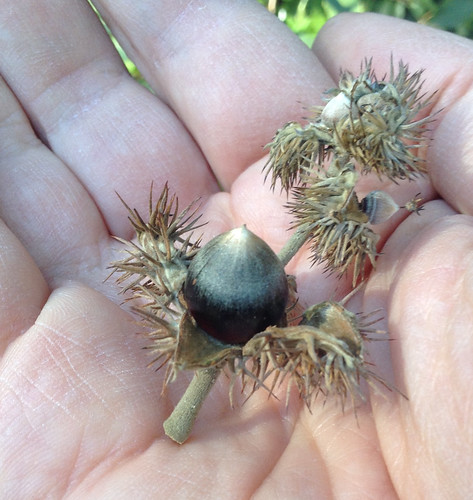

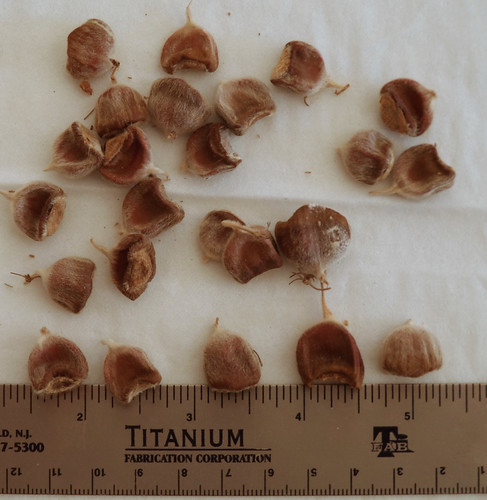
Close-up of shelled nuts. This picture was taken a month after they had ripened and so they've begun to dry out but are still edible.
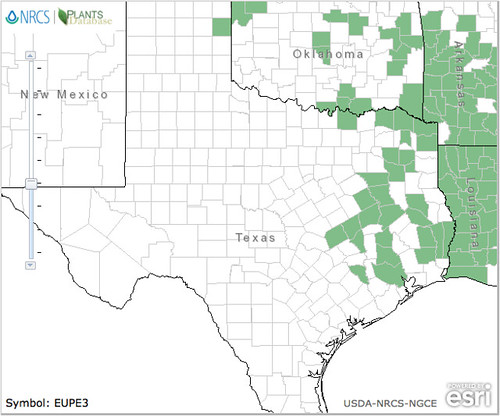
Texas distribution, attributed to U. S. Department of Agriculture. The marked counties are guidelines only. Plants may appear in other counties, especially if used in landscaping.
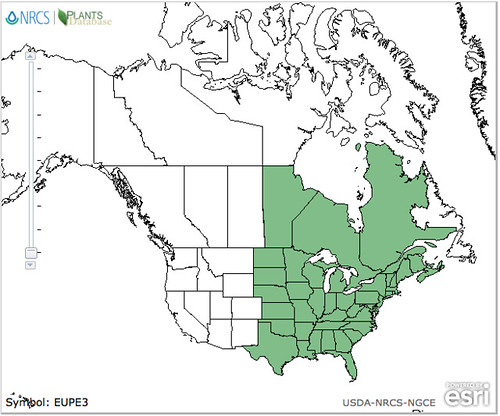
North American distribution, attributed to U. S. Department of Agriculture.

To stumble upon a stand of Allegheny Chinkapins is to stumble upon treasure. These large, usually multi-trunked bushes/small trees suffered from Chestnut Blight leading to reduced numbers across much of North America. A rare stand can still be found growing under larger trees in the sandy soil of tall banks overlooking water. The sandy soil gives them the drainage they need to avoid root-rot while the larger trees partially protects them from the fierce Texas sun. The long, narrow, sharply-toothed leaves, deep green on top and pale underneath, are arranged in an alternate pattern along the branches. In the spring long clusters of small, tan-yellow flowers hang from the tree. By fall these clusters have been replaced with sharp, spikey pods, each containing what looks like a small acorn.
Harvesting these nuts takes some work as they cling to the tree and are protected by the sharp, spiny remains of their outer husks. One usually has to carefully pick nuts off the shrub/tree one by one. You are likely to find some of the nuts have already germinated while still attached to the tree. Don't eat these but instead carefully plant them nearby.
Allegheny Chinkapin nuts lack tannins or other bitter compounds and so have a sweet, nutty flavor when eaten raw. Being so rare, limit yourself to just a nut or three. Take a few more to plant in similar locations so as to try and bring back this amazingly delicious treat. Animals love these nuts so getting them before squirrels, raccoons, possums and the such is tricky.
Like chestnuts, Allegheny Chinkapin nuts can be roasted to give almost a chocolatey sort of flavor. Place the uncracked nuts on a cookie sheet in an oven at 350F. After five minutes pull out a nut, crack it open and taste it. The roasting time is a personal preference but if the nuts' shells begin cracking it's definitely time to pull them out.
If you do over-roast the nuts they can still be used to make a caffeine-free coffee substitute. Grind the shelled nuts in a coffee grinder then either use them as is or combine them with real coffee to make a pot of brown, somewhat bitter fluid.
Buy my book! Outdoor Adventure Guides Foraging covers 70 of North America's tastiest and easy to find wild edibles shown with the same big pictures as here on the Foraging Texas website.