Scientific Name(s): Juniperus ashei, Juniperus virginiana
Abundance: common
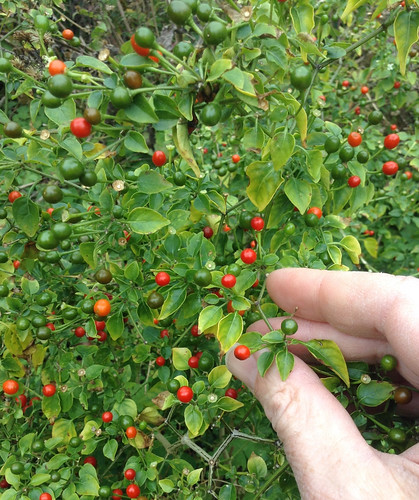
What: leaves, berries
How: leaves see below; berries as seasoning, infused, tinctured, or raw.
Where: landscaping, arid, woods, borders, fields
When: spring, summer, fall, winter
Nutritional Value: low
Dangers: Leaves of Juniperus virginiana, which contain thujone, which slows down the liver's removal of alcohol.
Medicinal Summary:
Inner Wood - soothes skin inflammations; kills scabies (
salve, tisane)
Leaves - tea soothes respiratory and gastrointestinal inflammations; soothes indigestion; diuretic; relieves bloating; soothes painful menstruation; eases chronic rheumatism; antibacterial; antifungal (used as a
tisane, elixir, oxymel)
Red Cedar (Eastern Redcedar - Juniperus virginiana) Structural Features:
Leaf Arrangement: The leaves are arranged in whorls of three, forming scale-like or needle-like structures.
Leaf Shape: Leaves are scale-like, measuring around 1/16 to 1/8 inches in length.
Leaf Color: Foliage can range from green to blue-green, depending on factors like age and environmental conditions.
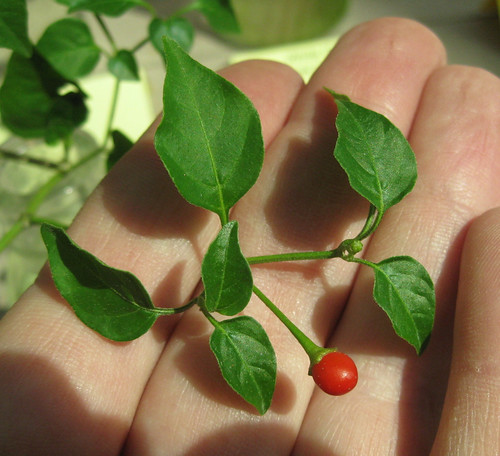
Fruit (Seed Cones): Red cedar trees produce small, berry-like cones that are about 1/4 to 1/2 inches in diameter. The color is bluish-purple on mature trees.
Bark: Bark is reddish-brown, fibrous, and peels in strips. On older trees, it becomes gray and scaly.
Height: Red cedar trees can grow up to 40 to 50 feet in height.
Hairs: Leaves and branches are generally smooth, without noticeable hairs.
Wood Color: Heartwood is typically reddish-brown.
Wood Use: Valued for its aromatic, insect-repelling wood, often used for cedar chests and closets.
Branching Pattern: Red cedar trees have a pyramidal or columnar shape with dense foliage.
Texas Mountain Cedar (Ashe Juniper - Juniperus ashei) Structural Features:
Leaf Arrangement: The leaves are arranged in whorls of three, forming scale-like structures.
Leaf Shape: Leaves are scale-like, measuring around 1/8 to 1/4 inches in length.
Leaf Color: Foliage can range from green to blue-green.
Fruit (Seed Cones): Texas mountain cedar produces small, berry-like cones that are about 1/4 to 1/2 inches in diameter. The color is bluish-purple on mature trees.
Bark: Bark is typically reddish-brown and peels in long, fibrous strips.
Height: Texas mountain cedar trees can reach heights of 30 to 50 feet.
Hairs: Leaves and branches are generally smooth, without noticeable hairs.
Wood Color: Heartwood is typically reddish-brown.
Wood Use: The wood is aromatic and used for various purposes, including fencing and woodworking.
Branching Pattern: Texas mountain cedar trees have irregular branching and a dense, rounded crown.
Juniperus ashei aka Mountain Cedar in the Hill Country. Note the round shape.

Juniperus ashei generally have multiple trunks.

Juniperus ashei about to release LOTS of pollen!

Juniperus ashei, berries which take several years to mature.

Both mountain and red cedar have alternating leaves that are tiny, tough, and closely overlap like scales.

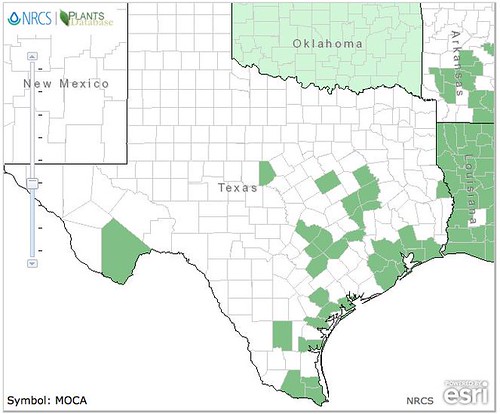
Texas distribution of Junipers ashei, attributed to U. S. Department of Agriculture. The marked counties are guidelines only. Plants may appear in other counties, especially if used in landscaping.
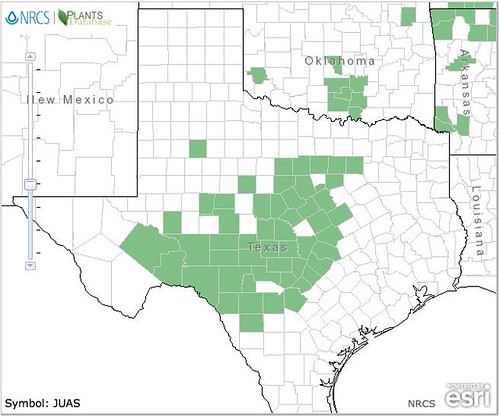
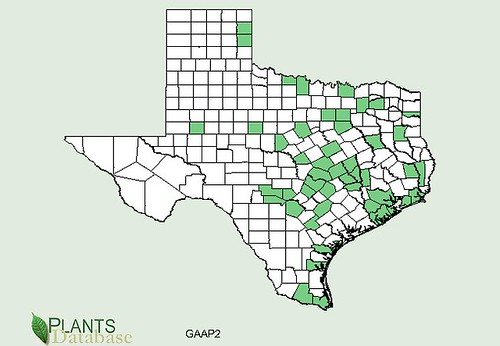
North American distribution of Junipers ashei, attributed to U. S. Department of Agriculture.
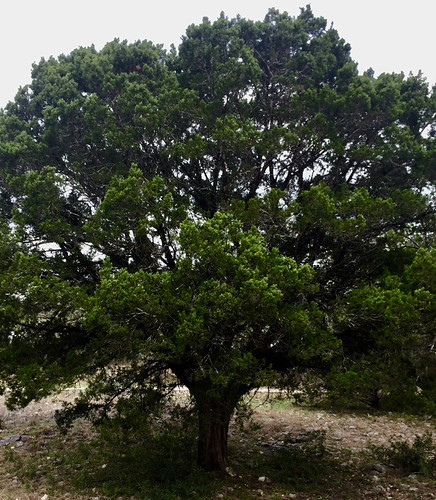
Juniperus virginiana aka Red Cedar. Note the pyramidal shape.

Juniperus virginiana berries are high in sugar and are eaten as a trail snack, though their flavor is somewhat intense.
Closeup of Juniperus virginiana berries. The gray color is wild yeast that can be used to raise bread or make alcohol.

Juniperus virginiana generally form only one trunk. Bark peels off easily and makes good tinder.

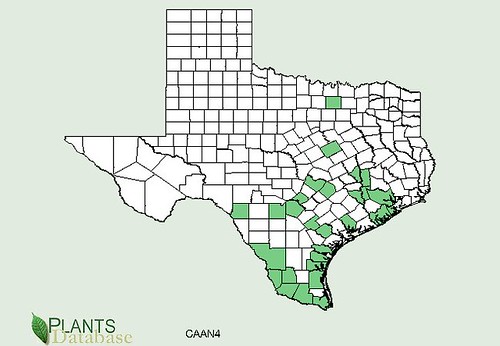
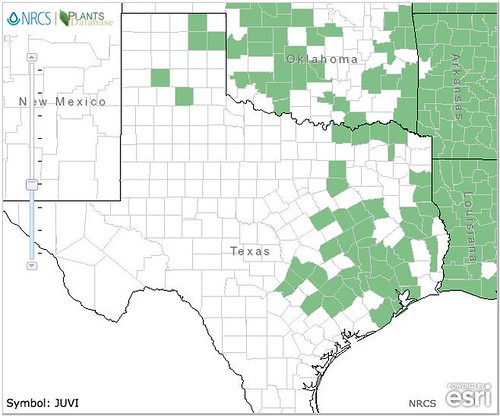
Texas distribution of Junipers virginiana, attributed to U. S. Department of Agriculture. The marked counties are guidelines only. Plants may appear in other counties, especially if used in landscaping.
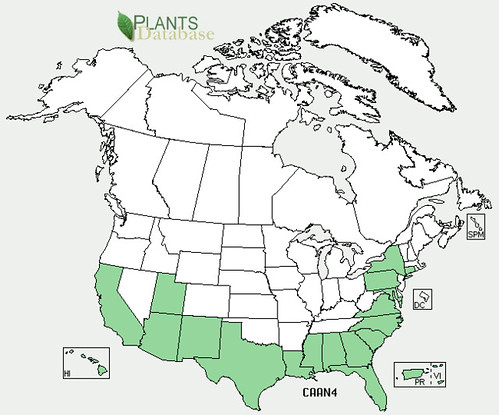
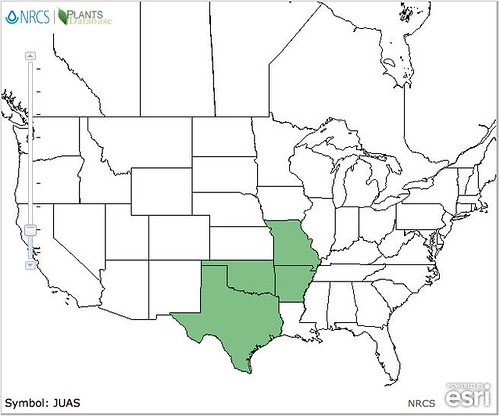
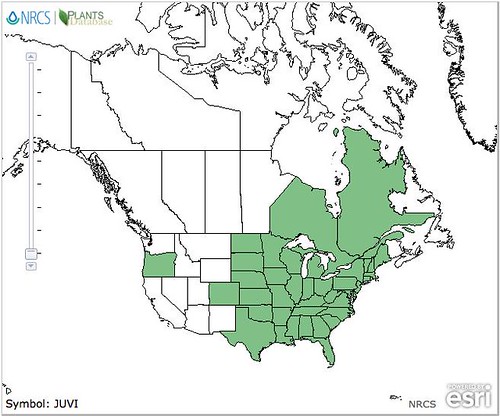
North American distribution of Junipers virginiana, attributed to U. S. Department of Agriculture.
First things first, junipers and cedars are the same thing. That being said, there are two types of cedar trees in Texas. The first, Junipers ashei, is the small, multi-trunked Hill Country cedar sometimes referred to as Mountain Cedar which takes on a roundish shape. More to the east and northern parts of Texas you'll find the Red Cedar (Juniperus virginiana) which has a single trunk and grows quite tall with a pyramidal shape. The trunks of both are covered with loosely peeling, fibrous bark. The inner wood of both is reddish in color and very aromatic. When used in campfires it'll "pop" a lot and throw sparks.
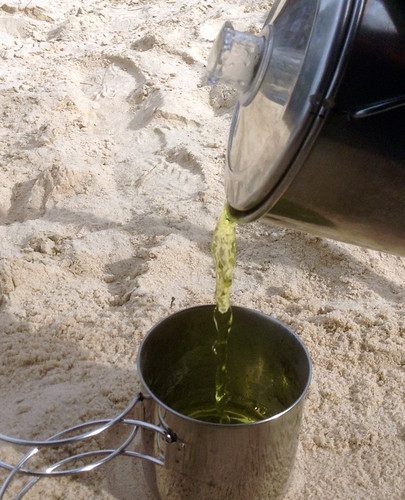
The Hill Country cedars, Juniperus ashei, can be used in multiple ways. Starting with the leaves, they can be smoked, made into tea, or used to infuse vinegar. Native Americans smoked the leaves both for pleasure and medicinally to help with lung and sinus issues/infections. Cedar tea contains the anti-viral compound known as deoxypodophyllotoxin which may be why such tea was historically used to treat many viral-based diseases. The berries, which are not true berries but rather a very strange cone like a pine cone, can be nibbled raw but they have a very potent flavor so the are best used in small quantities as a flavoring agent or seasoning. German settlers loved to ad 2-4 berries to each quart of sauerkraut. Gin alcohol is made by adding juniper/cedar berries during or after the distillation step. Soaking the berries in vodka for a few weeks creates your own version.
My favorite thing to do with J. ashei is to infuse apple cider vinegar with it to make a "forager balsamic vinegar. To do this take a fresh, 16oz bottle of apple cider vinegar and pour off 1/2 cup. Now take a bunch of fresh J. ashei leaf-tips and start twisting and smashing them...not too much as you don't want lots of little pieces. Just enough so that their oils can steep into the vinegar. Now start adding these abused cedar leaf-tips into the bottle until the vinegar is just about to overflow. Cap it and set it somewhere dark for 6-8 weeks, shaking it at least once a day. After the required time has passed strain out the leaf bits through a coarse wire mesh. Don't use filter paper as you'll want the original vinegar solids to remain in the liquid. I add a sprig of cedar into the strained bottle just to mark it as infused.
Now let's talk about Red Cedar (Juniperus virginiana). While it's berries (okay, cones) can be used the same as Junipers ashei's berries, the leaves should not be used to make tea, infused vinegars, or smoked. These leaves contain several compounds such as thujone which can cause diarrhea if consumed in large quantities. Yes, thujone is also the active ingredient in absinth, but that's none of my business. Thujone slows down the removal of alcohol from the blood so just a little bit of it cause the BOC to shoot up much higher than expected from a drink. Now, that all being said, there is historical records of the Juniperus virginiana being used for tea so like so many wild edibles.
Buy my book! Outdoor Adventure Guides Foraging covers 70 of North America's tastiest and easy to find wild edibles shown with the same big pictures as here on the Foraging Texas website.