Abundance: common
What: flowers, berries
How: the flowers can be eaten raw or fried as fritters, the berries are best when cooked into muffins/pancakes/waffles, made into jam or wine
Where: edges, wet areas
When: summer
Nutritional Value: Vitamin A & C, calcium, iron, sterols, and flavonoids.
Dangers: all other parts of plant (bark, leaves, wood) are poisonous. Berry clusters must be flat, kind of like cauliflower, not rounded like a globe. Compounds in elderberry flowers and berries can disrupt chemotherapy drugs.
Medicinal Summary:
Flowers, Berries - immune system stimulant (syrup, tincture, tisane)
Stands of elderberry can be 12'-14' tall.


Elderberries along a stream bank.

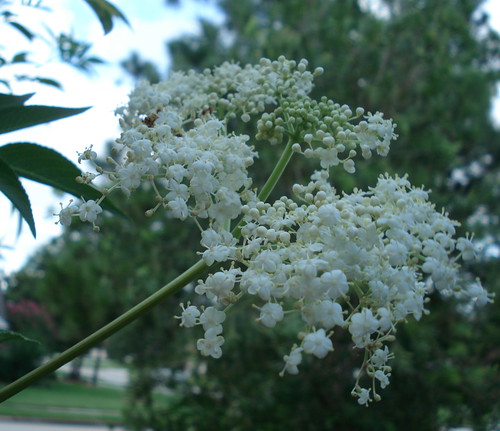
The flowers start out as small, light-green balls then open up into white/cream flowers with five petals.

The flower clusters are shaped kind of like cauliflower in an "umbel" (aka umbrella shape).

Flowers (edible).

Close-up of flowers after harvesting.


Dark purple-black fruit (edible dry or cooked, not raw).


Close-up of compound (multi-leaflets) leaves (topside).

Close-up of compound leaves (underside).

By the end of summer the leaves can become very complex.

Stem/trunk of Elderberry. The spots where from leaves growing from the stem in previous years.

Getting ready to make a batch of Grandpa's "Cure's what ails ya!" (Godzilla movie not required). Directions below.
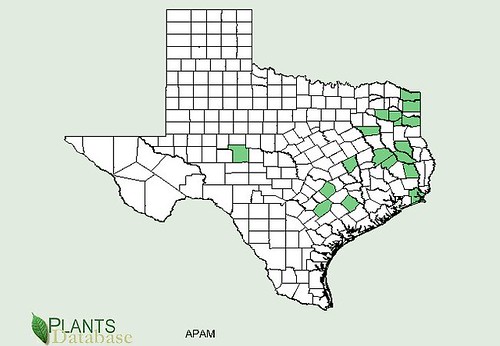
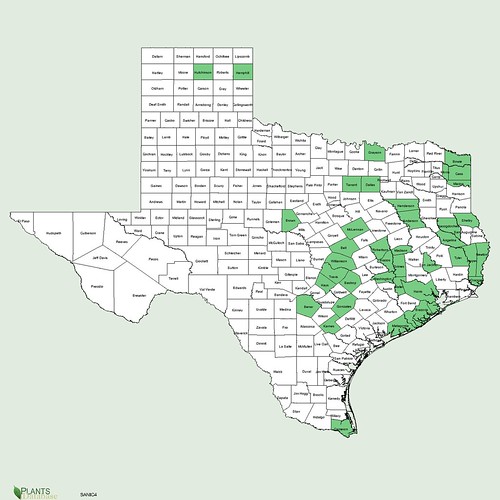
Texas distribution, attributed to U. S. Department of Agriculture. The marked counties are guidelines only. Plants may appear in other counties, especially if used in landscaping.
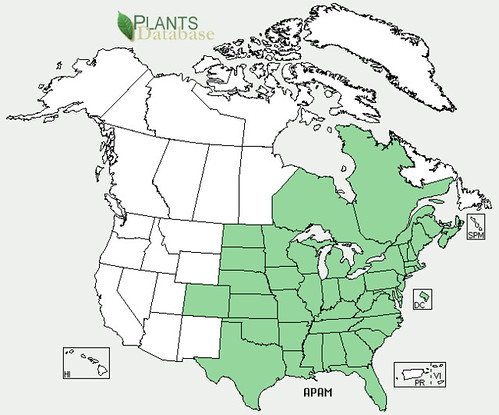
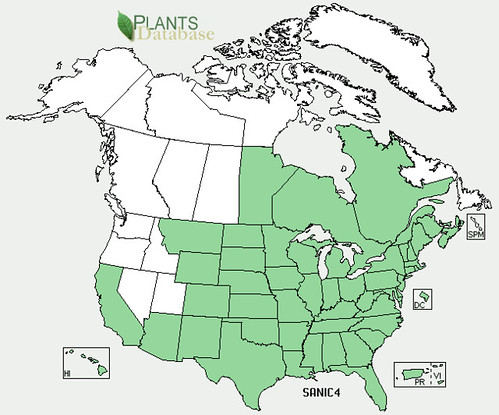
North American distribution, attributed to U. S. Department of Agriculture.
Stands of elderberry are most common along streams and other moist areas. Standing approximately 10 feet tall with compound leaves and green-to-gray, bumpy bark and white pithy interiors, elderberries are distinctive shrubs or small trees. The cauliflower-shaped clusters of white flowers appear in early spring, flowered by clusters of green and then dark purple berries. The plant will continue to produce flower clusters through the summer and berries into early fall. One has to be quick to gather the berries as birds love them!
The elderberry flowers are a good raw snack, eaten right off the tree. Other popular uses include adding the flowers to muffins, pancakes, frosting and batter-frying them into fritters. They can also be used to flavor assorted non-alcoholic and alcoholic drinks.
The berries do NOT taste great raw due to the presence of a rather off-putting volatile oil. However, drying or cooking the berries drives off this chemical resulting in a really good flavor. Add the berries raw or dried berries to pancakes, muffins or other batter-style cooked goods. Elderberry jam and jelly is an old-time favorite. Of course, the most popular way to use elderberries is to make wine!
My grandfather used to make great elderberry wine. He also made a general illness preventative/cure medicine called "Cure's what ails ya!" from the flowers by filling a 1 quart canning 1/3 to 1/2 full with fresh elderberry flowers (no stems!) then adding 1 tablespoon of sugar, two shots of Triple Sec orange liquor and filling to jar almost to the top with vodka. The jar was sealed tightly then shook twice a day for 6-8 week. At that point the solids were strained out and the fluid transferred into a tightly capped bottle. I am NOT giving medical advice but two shoots of this was our family treatment when we felt an illness coming on. Western science suggests elderberry flowers and berries contain the immune-system stimulating molecule "Sambucol" which can also be bought over the counter in pharmacies for use in fighting viral infections. Please note that if you are on immune system suppresants, such as after an organ transplant or if you suffer from an auto-immune disease, you should avoid consuming elderberry products.
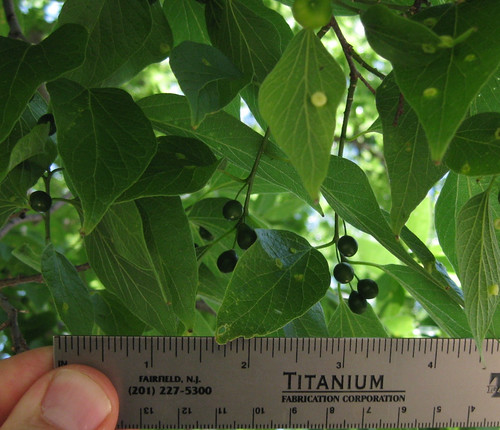
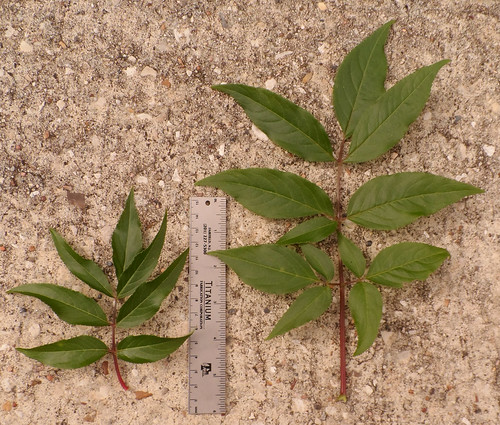
There are two plants people often mistake for elderberry, Chinese Privet (Ligustrum sinense) and Arrowwood (Viburnum dentatum). Chinese Privet is slightly toxic and has simple rather than compound leaves though they are all lined up so as to look a little like the compound leaves of elderberry, but smaller and not pointed at the end. Chinese Privet fruit appears in the fall/winter in grape-like clusters of dark, purple, somewhat football-shaped berries instead of the umbels of elderberry berry clusters.
These are Pokeweed berries which are deadly. Note that they grow in a column rather than an umbrella-shape.

Chinese Privet berries and leaves. This plant is commonly mistaken for Elderberry but it is POISONOUS.
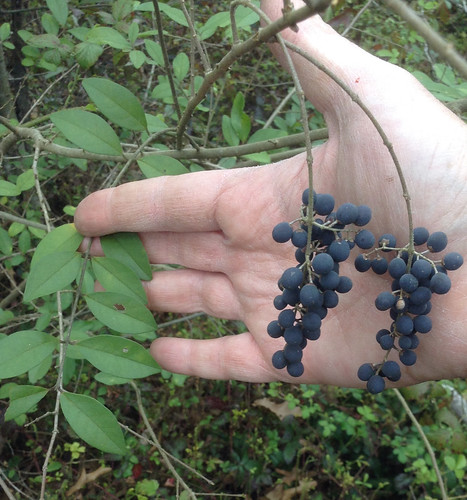


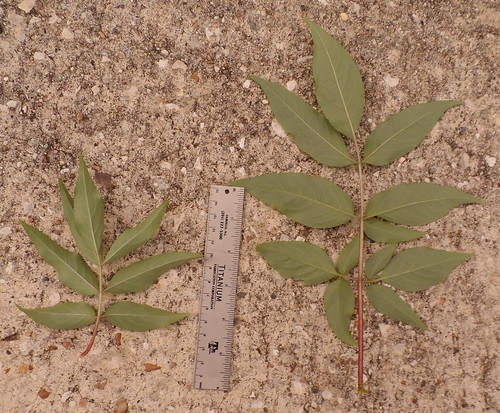
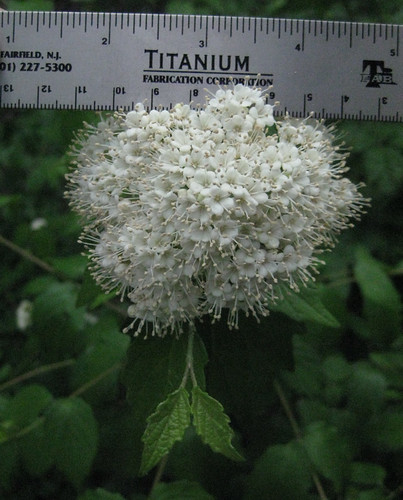
Arrowwood (Viburnum dentatum) produce umbel-shaped clusters of small, white flowers that look just like elderberry flowers but as with the Chinese Privet, Arrowwood leaves reveal its true identity. Arrows leaves are simple, oppositely-opposed along its branches and have toothed edges. After the flowers pass umbel-shaped clusters of grayish-purple, football-shaped berries ending in little dried flower bits appear. These fruit are edible but tasteless.
Arrowwood flowers (edibility unknown...so don't eat them).

Arrowwood leaves (not edible).

Arrowwood berries (edible but tasteless).

Buy my book! Outdoor Adventure Guides Foraging covers 70 of North America's tastiest and easy to find wild edibles shown with the same big pictures as here on the Foraging Texas website.