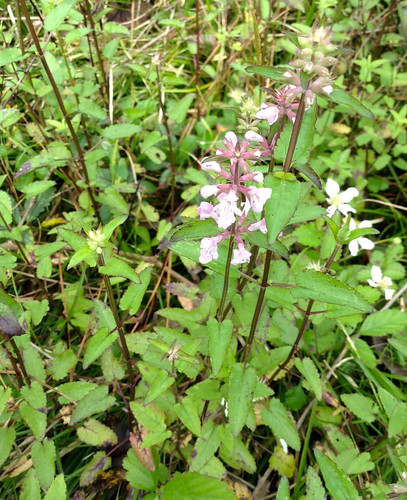
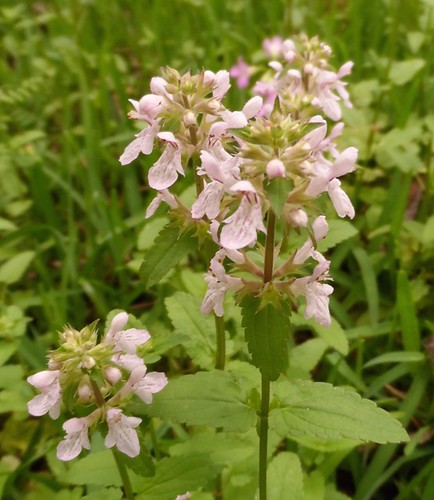
Abundance: plentiful
What: nuts, leaves
How: roast nuts, used leaf as seasoning
Where: woods, borders
When: leaves all year, nuts in the fall
Nutritional Value: Calcium, iron, other minerals, vitamins A, C, B6, folate.
Other uses: nuts contain a mild stimulant
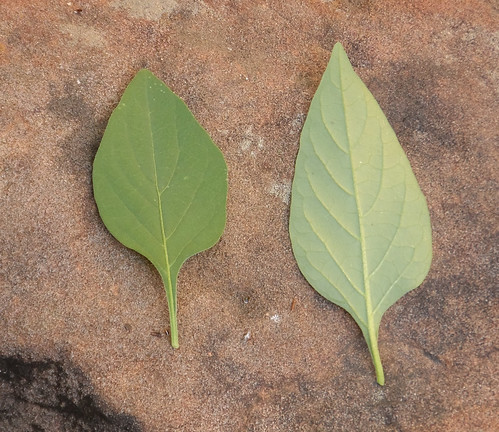
Dangers: Looks similar to the very poisonous cherry laurel. The leaves of cherry laurel smell like cherry/cyanide and have toothed edges while bay laurel leaves have smooth edges and smell like Italian seasoning.
Medicinal Summary:
Leaves - aid digestion; reduces bloating from gas; soothes skin, urinary tract and bronchial inflammations (tisane)
Laurus nobilis (Sweetbay) Structures:
Young tree. They get much bigger with time.
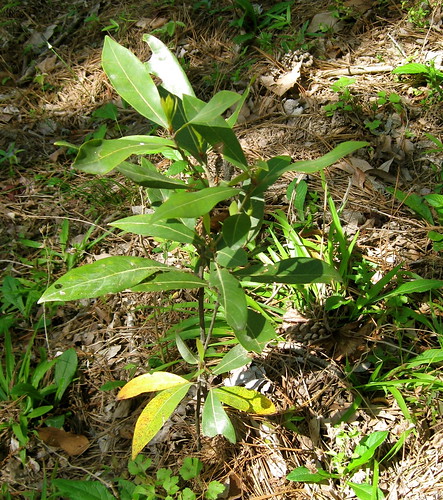


Much older, larger bay tree!

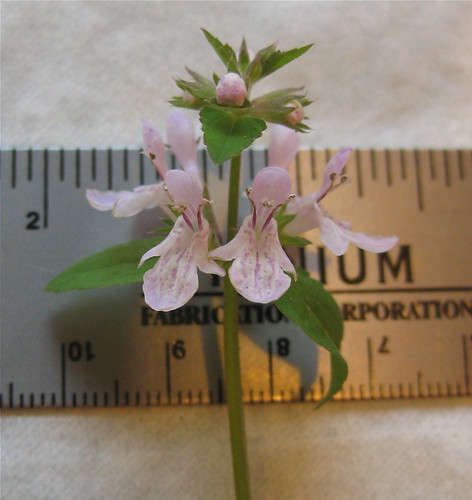
Leaves closeup (Bay Laurel leaves have smooth edges)

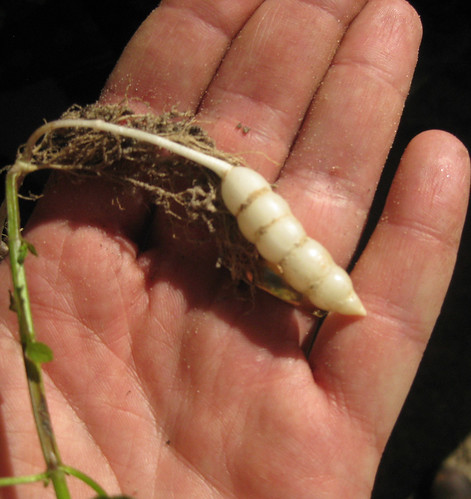
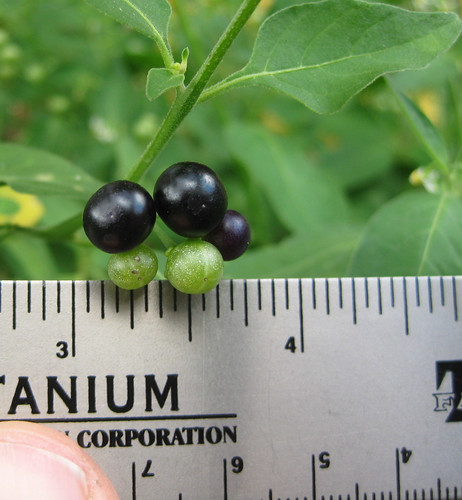
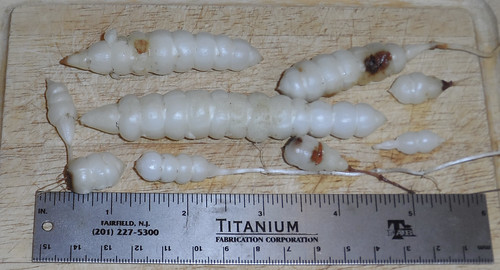
Nuts

Dead leaves on a bay tree suffering Laurel Wilt. This fungal disease is transferred by an alien beetle and is wiping out our native bay trees. Currently there's no cure. :-(

Teeth (pointy bits along edge of leaves) + cyanide/cherry smell = poisonous cherry laurel. DO NOT EAT CHERRY LAUREL!!

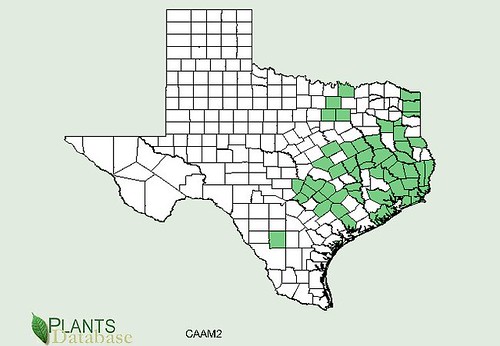
Texas distribution, attributed to U. S. Department of Agriculture. The marked counties are guidelines only. Plants may appear in other counties, especially if used in landscaping.
I know these can be found in Montgomery County, TX.
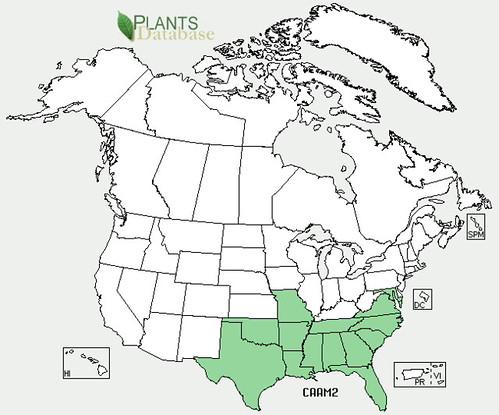
North American distribution, attributed to U. S. Department of Agriculture.

Texas has multiple types of bay trees. Around Houston the most common are sweet bay (Laurus nobilis), redbay (Persea borbonia) and laurel cherry (Prunus caroliniana). All three grow in the same environment, preferably as understory trees in moist, shaded areas. Very slow growing, most you’ll find will be small trees around 20’ tall. However, mature trees can rival oaks in size and appearance. Crushed sweet bay and redbay leaves have a wonderful bay aroma while laurel cherry smells like bitter almonds or artificial cherry scent. That bitter almond smell is poisonous cyanide and the so the leaves of the laurel cherry should not be used as a seasoning or consumed in any other manner.
Besides scent, the toxic laurel cherry trees can be distinguished from safe sweet bay and redbay by the edges of their leaves. The sweet bay and redbay leaf edges will be smooth while the dangerous laurel cherry leaves will have teeth, ranging in number from two very small ones near the base to many all along the leaf edge.
The leaves of the sweet bay and redbay are available all year long and are added to sauces and other foods where one would traditionally use bay leaves. They do have a very potent flavor, so you usually don't need to add more than 3-4. They can be used fresh or dried. Add the leaves while cooking but remove them before serving as no bay leaves should actually be eaten. Supposedly these stiff, hard leaves can penetrate an intestine.
In the fall the dark nuts are toasted and then nibbled on as a strongly-flavored snack. Remove the soft flesh from the bay nut then roll the nuts around in a very hot pan until they start to split open. Remove the outer brittle husk then return the inner meat back to the pan for a final toasting. No oil or grease is needed. These toasted nuts can also be ground and used as a seasoning. 3-5 of these roasted seeds, when boiled in water then adding nutmeg and cinnamon make a very pleasant drink which tastes somewhat like coffee.
Our bay trees are currently under grave attack by a fungal disease transmitted by the invasive, Asian beetle Xyleborus glabratus. This fungal infection first shows up by branches dying and their leaves turning brown. Eventually the whole tree will die, taking with it the main birthplace of Palamedes Swallowtail butterflies. So this disease may not just wipe out one of the south's most common trees, it may also drive that butterfly to extinction, too.
Buy my book! Outdoor Adventure Guides Foraging covers 70 of North America's tastiest and easy to find wild edibles shown with the same big pictures as here on the Foraging Texas website.