Scientific name: Taraxacum officinale
Abundance: common
What: leaves, flowers, roots
How: young leaves in salad or boiled; flowers are used in wine; roots are roasted to make a coffee substitute or boiled for twenty-thirty minutes before eating
Where: yards, sunny
When: spring, early summer
Nutritional Value: Vitamins A, B, thiamine, riboflavin, minerals, and protein
Medicinal Summary:
Flower - wound healer (
salve, infused oil)
Root/Leaves - diuretic; antibacterial; laxative; sedative; appetite stimulant (
poultice, tisane, tincture)
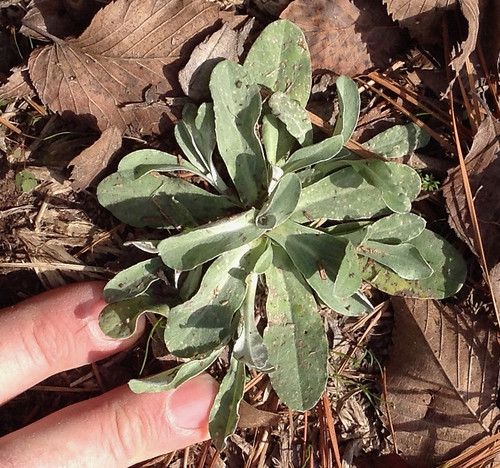
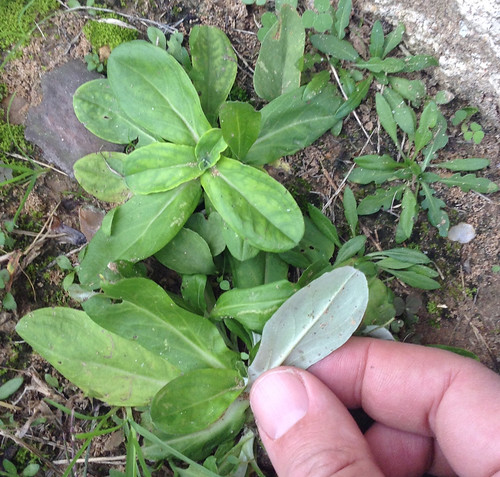
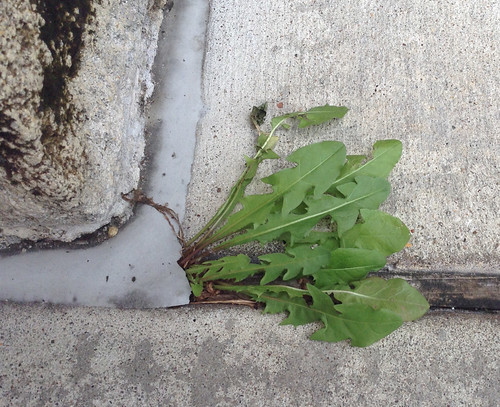
Leaf Shape: The leaves of a dandelion are spatulate to oblong, often deeply lobed with the asymmetrical lobes pointing back towards the base of the leaf, giving them a jagged appearance.
Venation: Dandelion leaves exhibit pinnate venation, with a central vein running the length of the leaf and smaller veins branching off to the sides.
Leaf Margin: The margins of the leaves are irregularly toothed or lobed, often described as dentate or runcinate (sharp lobes).
Leaf Color: They are a dark green color, sometimes with a hint of red or purple.
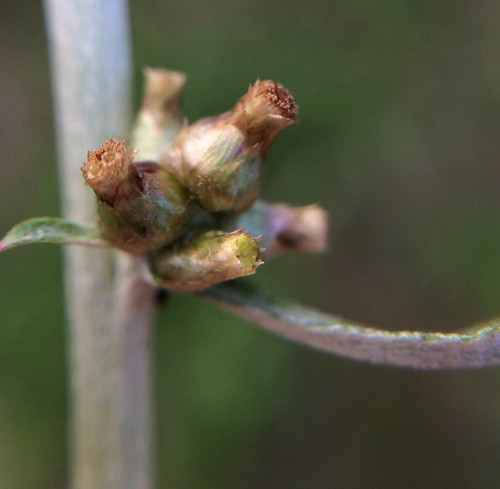
Flower Structure: Dandelions have a single flower head on a hollow stem; each head is actually made up of many tiny flowers called florets. Stamens tops are split, often into two spirals.
Flower Color: The flowers are bright yellow supported by a dark green calyx.
Fruit: Small, dry, one-seeded fruits (achenes) attached to a parachute-like structure called a pappus.
Seeds: Each with a pappus for wind dispersal, resembling a small, brown, elongated seed.
Stem: Hollow, leafless, and milky, typically 6 to 24 inches tall.
Stem: The stem is hollow, smooth, and exudes a milky sap when broken.
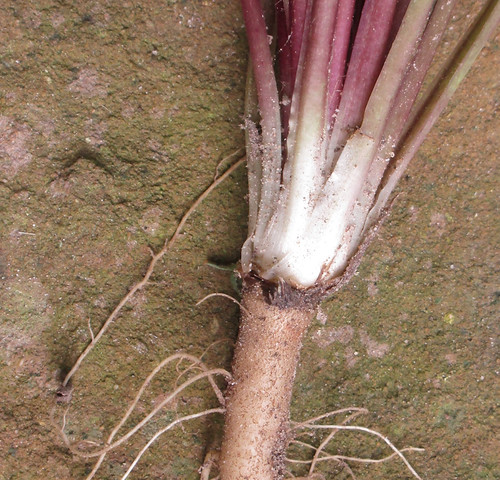
Roots: Extremely long (12 feet!) taproots that are tan on the outside and white/off-white inside. Surface of root will be covered with fine rootlets.
Hairs: There are no hairs on the leaves of the dandelion but the flower stems may have fine hairs.
Height: When in flower, dandelions typically reach a height of 2 to 18 inches.
Single dandelion plant.


Dandelions are very persistent!

Cluster of dandelion plants, flowers, and seed-heads.

Perfect time to harvest dandelion leaves, just before any flower stems appear.

You only want to use the yellow and white parts of dandelion flowers. Their green collar is extremely bitter and must be removed.
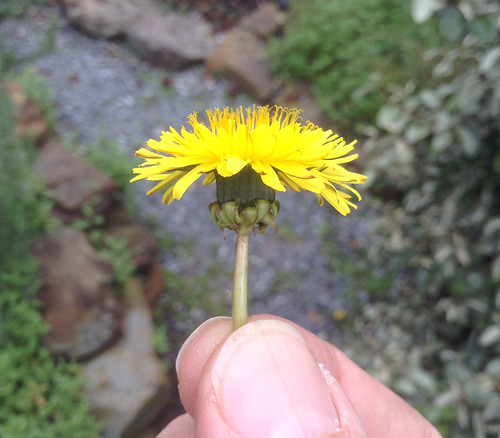

Close-up of Dandelion flower. Note how the stamens split into two curls at the top.

Dandelion flower stems are hollow, may have fine hairs, and end in a single flower.

A mature dandelion root can be twelve feet long! This one was a little over one foot.

The best part of dandelions for eating are the white leaf stems right at the top of the root, sautéed in some bacon grease!

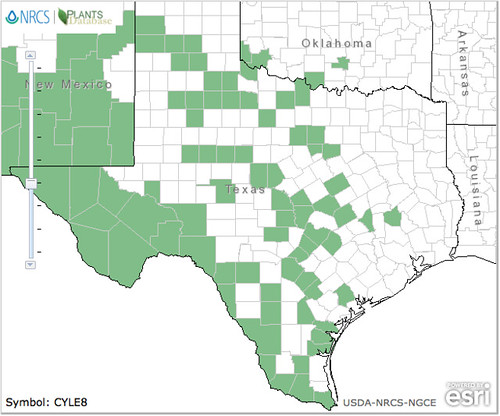
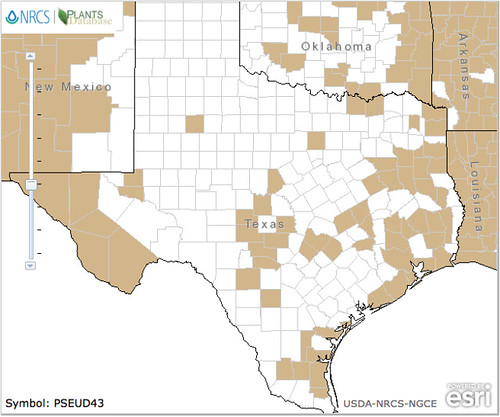
Texas distribution, attributed to U. S. Department of Agriculture. The marked counties are guidelines only. Plants may appear in other counties, especially if used in landscaping.

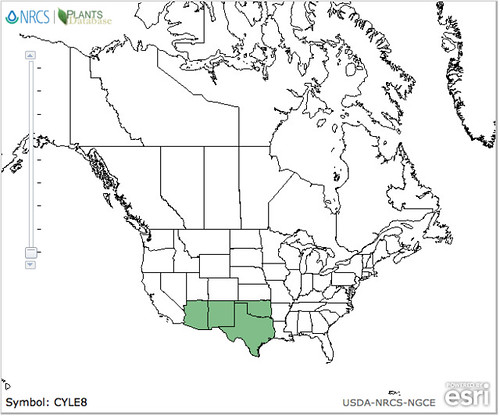
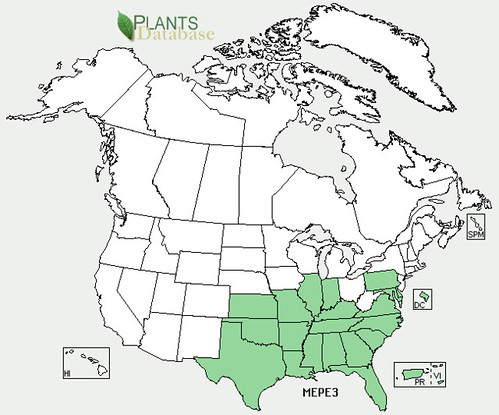
North American distribution, attributed to U. S. Department of Agriculture.
Dandelions are one of the superfoods of foraging due to their high amounts of vitamins, minerals, and protein as well as the multitude of ways to use them. However, these nutrients come at a cost, mainly the strong bitter flavor of this plant.
This bitterness can be tamed via several different methods. The easiest is just to boil the leaves in several changes of water to extract the bitter compounds. This will remove a small amount of the nutrients and the resultant leaves are not very visually appealing.
If you have access to milder greens with which to make a salad then "dilute" a small amount of shredded dandelion leaves with a much large amount of mild greens. 1 part dandelion + 9 parts mild greens is a good ratio.
Wilting the dandelion greens with hot bacon grease is perhaps the most flavorful method. The hot grease both destroys some of the bitter compounds as well as coats and "desensitizes" your tongue to the bitterness. This is my favorite treatment. Note that olive oil will also work though not quite as well.
Overwhelming the bitterness with (sour) vinegar and or salty (soy sauce) flavors also works. A strong vinegar/oil salad dressing with the dandelion greens works very well.
The yellow flowers can be used to make wine, tea, or dress up a salad. Remove the extremely bitter, green bracts from the base of the flower though.
To make dandelion coffee you first need to collect a large bowl of dandelion roots. Scrub them to remove dirt, then roast them in an oven at 400 degrees F until they turn brown. The dark brown the darker the resultant coffee. Grind the browned roots in a coffee grinder and then you can use the results as you would regular coffee grounds. While this tastes just like normal coffee it does not contain any caffeine.
Here's another great source on how to grow and use dandelions:
Gardener's Path - DandelionsEdible Dandelion Mimics:
Dandelion
Cat's Ear
Chicory
Japanese Hawkweed
Sow Thistle
Texas Dandelion
Wild Lettuce
Buy my book! Outdoor Adventure Guides Foraging covers 70 of North America's tastiest and easy to find wild edibles shown with the same big pictures as here on the Foraging Texas website.