Abundance: common
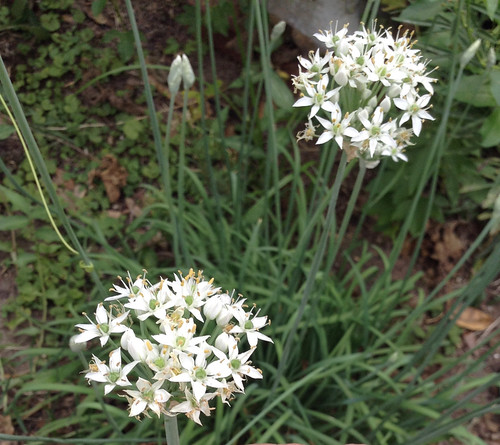
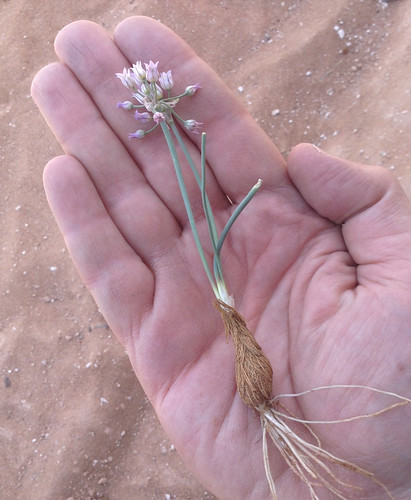
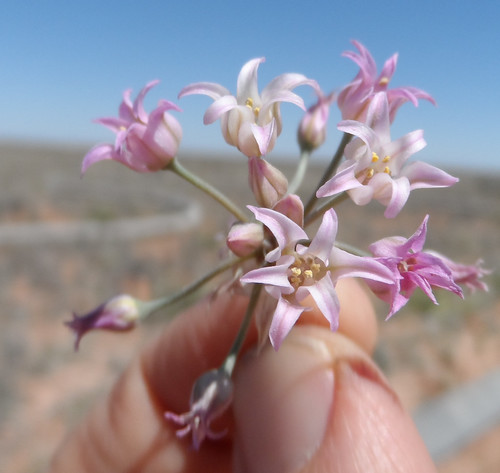
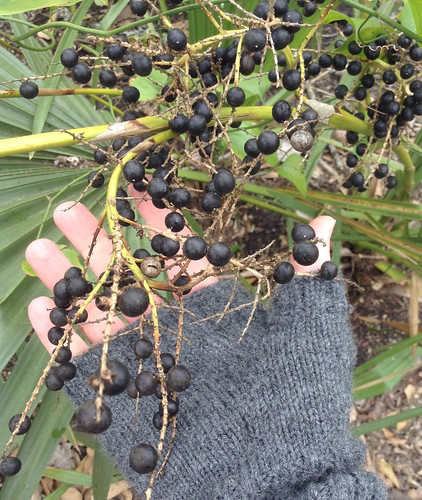
What: flowers, seeds
How: flowers for tea; seeds are ground into flour
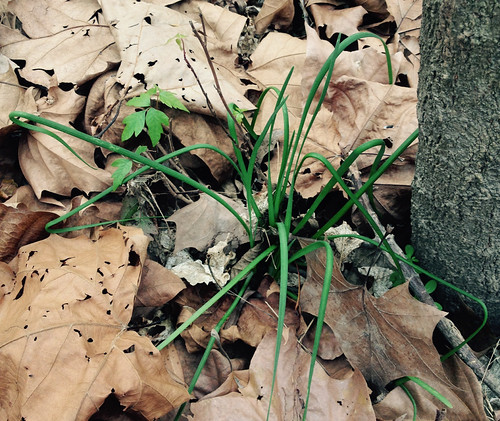
Where: southwest desert, hillsides, sunny, arid
When: flowers in late winter through spring, seeds spring to early summer
Nutritional Value: assorted vitamins from flowers, calories from seeds
Dangers: very thorny
Medicinal Summary:
Outer Skin - improves lymph flow, especially in the pelvic region of the body; expectorant (tisane)
Ocotillo in the southwest Texas.

Rain causes ocotillo to produce short-lived leaves. These pictures were taken in April, at the beginning of their flowering season.

Immature ocotillo flowers along with mature leaves.

Close-up of immature flower buds.
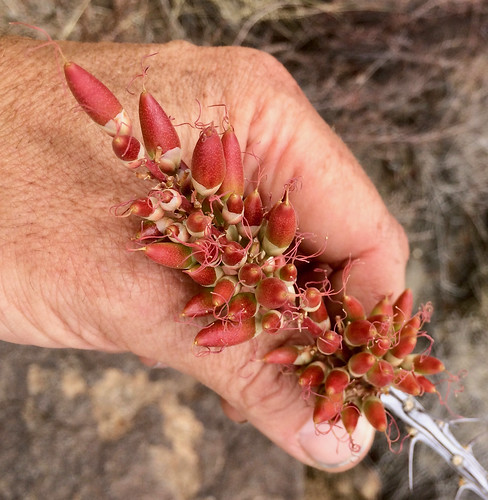

Close-up of ocotillo flowers.

Close-up of ocotillo stems along with Workman's Friend Barrier Skin Cream, a product made by the company for which used to work.

Texas distribution, attributed to U. S. Department of Agriculture. The marked counties are guidelines only. Plants may appear in other counties, especially if used in landscaping.
North American distribution, attributed to U. S. Department of Agriculture.
During most of the year the spiny, leafless ocotillo are often mistaken for a tall (up to twenty feet!), thin cacti. However, soon after a good rain small, rounded leaves appear though they don't last long. Once things return to a more arid state these leaves leave (ha ha ha!). Late winter through spring the tips of ocotillo branches will blaze with clusters of tubular, red flowers. This is a sign hummingbirds are passing through! Ocotillos and hummingbirds have co-evolved to be food source and primary pollinator, with the blooms being timed to feed hummingbirds just as they migrate through that local. An ocotillo transplanted or raised from seed will continue to bloom at the same time as it would in its source location, regardless of length of day, temperatures, or other common triggers for flower production.
Being loaded with power-giving nectar, a handful of the open flowers creates a sweet tea. Immature buds will result in a tart flavor and using too many will result in an exceedingly tart tea that'll likely be undrinkable. Keep in mind you're stealing food from hummingbirds so please harvest responsibly and minimally. About a month and a half after the flowers drop the seeds will be ready to harvest. Traditionally they were pounded into powder then boiled to make a porridge.
Accord to Charles W. Kane, ocotillo "bark" or outer layer contains a number of medicinal terpenes that improve lymph flow, especially in the pelvic region of the body. The tea works as a weak expectorant to dislodge hard to move phlegm as well as adding moisture to dry coughs.
Buy my book! Outdoor Adventure Guides Foraging covers 70 of North America's tastiest and easy to find wild edibles shown with the same big pictures as here on the Foraging Texas website.