Abundance: common
What: leaves, flowers, young fruit, root, seeds
How: raw, cooked
Where: disturbed areas, moist, sunny, fields, yards
When: spring
Nutritional Value: vitamins
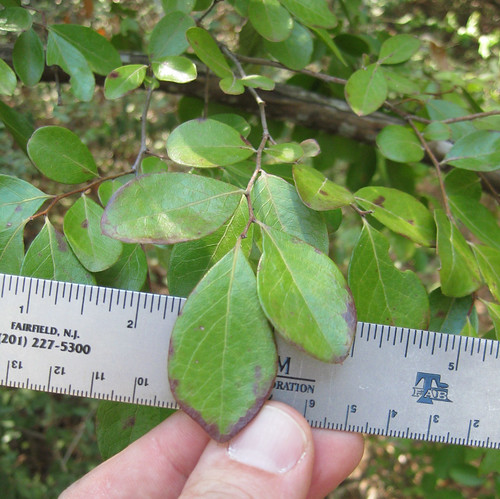
Dangers: don't mistake Carolina Geranium for Filaree.
Medicinal Summary:
Leaves/Flowers - antibacterial; antifungal; antiviral (interferon induction); antioxidant; anti-inflammatory; analgesic (tisane)
Texas Filaree (Erodium texanum) structural features:
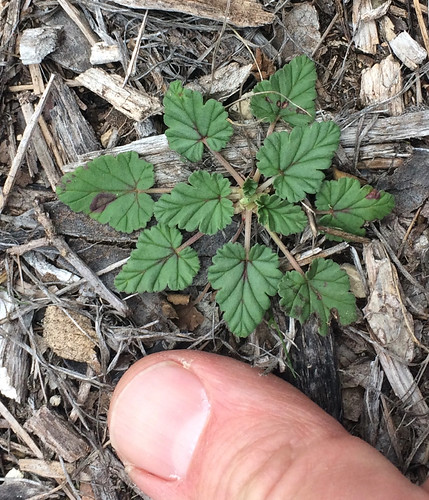
Texas Filaree (Erodium texanum) seeding.

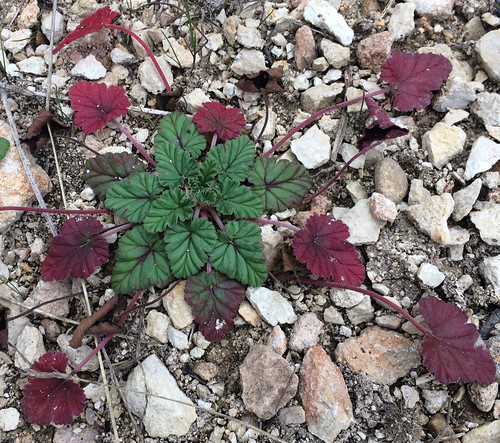
Slightly larger Texas Filaree. Those purple/red leaves are quite distinctive.

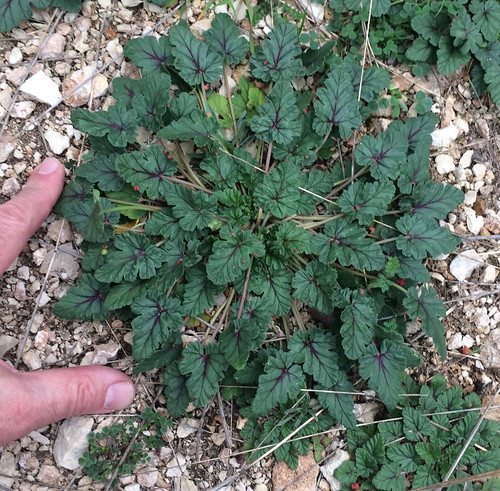
Still larger Texas Filaree (Erodium texanum).

Redstem Filaree (Erodium cicutarium) plants. Note the red growths on some of the leaves.
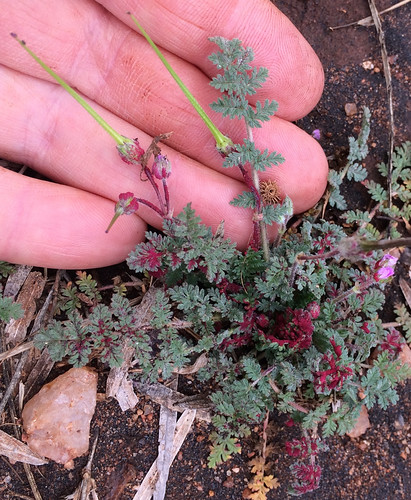


Close-up of Redstem Filaree (Erodium cicutarium) leaves.


Close-up of Redstem Filaree (Erodium cicutarium) flowers.

Close-up of Redstem Filaree (Erodium cicutarium) fruit that gives it its other name, 'Storkbill".
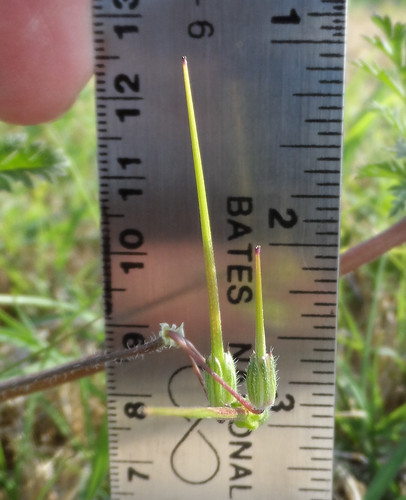


Redstem Filaree (Erodium cicutarium) seedling.

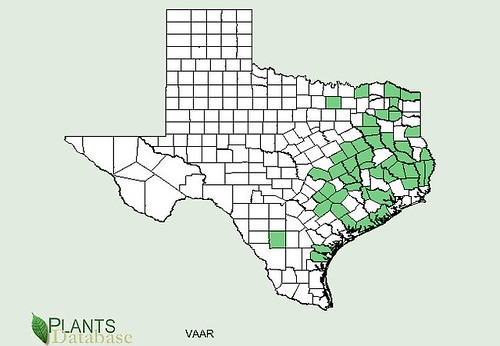
Texas distribution of Erodium texanum, attributed to U.S. Department of Agriculture. The marked counties are guidelines only. Plants may appear in other counties, especially if used in landscaping.
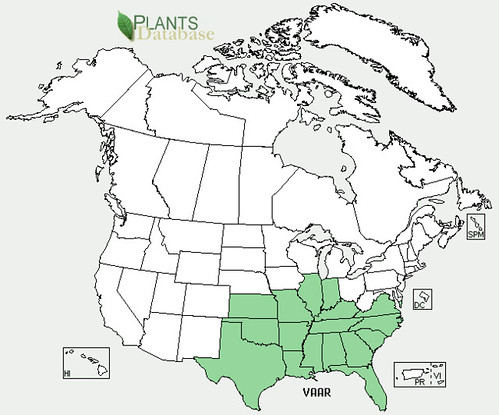
North American distribution of Erodium texanum, attributed to U. S. Department of Agriculture.
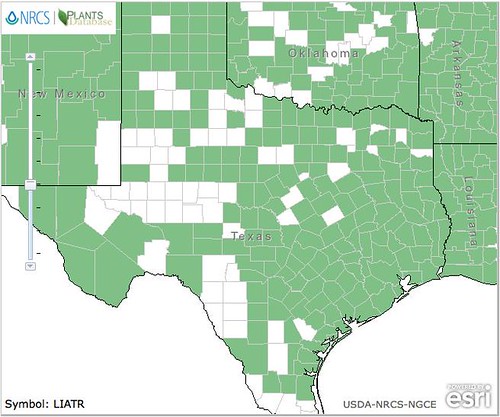
Texas distribution of Erodium cicutarium, attributed to U.S. Department of Agriculture. The marked counties are guidelines only. Plants may appear in other counties, especially if used in landscaping.
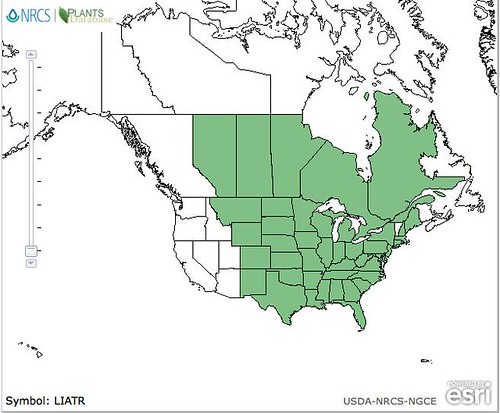
North American distribution of Erodium cicutarium, attributed to U.S. Department of Agriculture.
Plants define the ecological zones of Texas. Seeing the reddish, prostrate, rosettes of Filarree tell me the acidic soils of East Texas are shifting to the more alkaline, chalky soil of the Hill Country and farther west. Filler seems to thrive in damaged, barren soils such as walking/riding trails to the cracks in driveways and parking lots. This is one tough plant!
In most high-traffic places you'll find this plant it creeps low to the ground but in wilder, unmowed/untrampled areas it sends it's frilly, lobed leaves upwards along with its 5-petaled, purple flowers. The flowers grow in clusters at the ends of thin, hairy stalks. These flowers eventually turn into long 'beaked" seedpods that give these plants the alternative name of "Storkbill".
Pretty much all parts of this plant are edible, though it can be somewhat bitter raw. Cook the leaves like you would spinach or just steam them. The flowers are okay raw and while I suppose one could treat the seedpods like okra I have yet to confirm that. The seeds are actually quite nutritious with a good dose of vitamin K, according to Green Deane.
WARNING: Carolina Geranium (Geranium carolinianum) flowers and seedpods look slightly similar but it's not edible. The leaves of Carolina geranium are "hand" shaped whereas Filaree leaves are more "Christmas Tree" shaped.
Carolina Geranium flowers and leaves - too bitter to eat.

Carolina Geranium seedpods.

Carolina Geranium roots are strongly astringent and after being dried and powdered were placed in wounds to stop bleeding. The powdered Carolina Geranium roots were also gargled to sooth sore throats.
Buy my book! Outdoor Adventure Guides Foraging covers 70 of North America's tastiest and easy to find wild edibles shown with the same big pictures as here on the Foraging Texas website.