Abundance: common
What: flowers, leaves, maybe seeds
How: flowers pickled; leaves as tea; seeds...you're on your own!
Where: landscaping, woods
When: spring flowers, fall seeds, leaves all year
Nutritional Value:
Dangers: some sources list the seeds as edible others list them as poisonous
Medicinal Summary:
Seeds - anti-tumor; anti-inflammatory; anti-bacterial; anti-seizure; sedative (tincture)
Leaves - anti-cancer; antibacterial (tisane, tincture)
Magnolia tree. Note the green tops and brown undersides of the leaves.

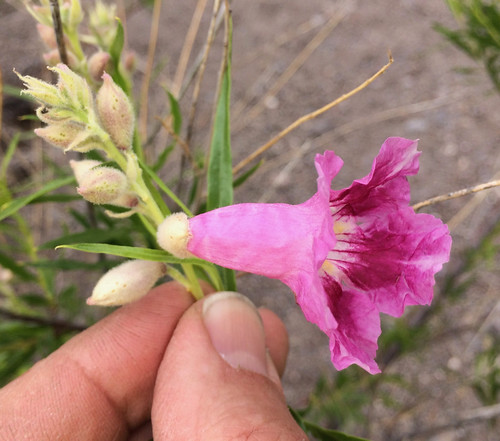
Magnolia flower buds.

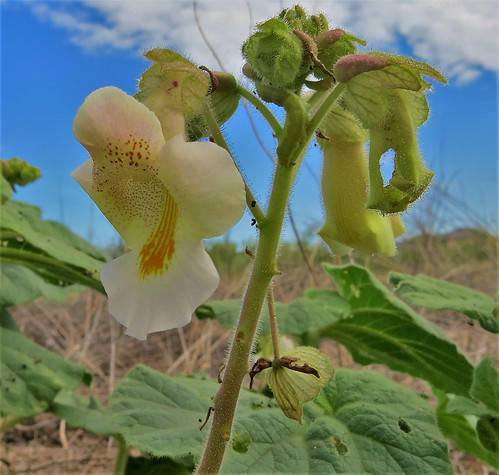
Flower beginning to open which I feel is the best time to pick them for use.

Open flower. Soon after they open the petals begin turning brown. I don't harvest them once several petals have become spotted.

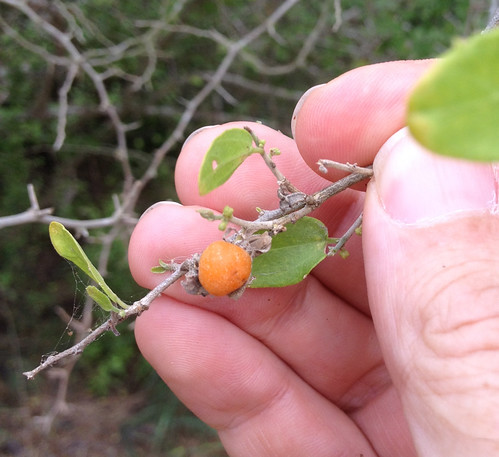
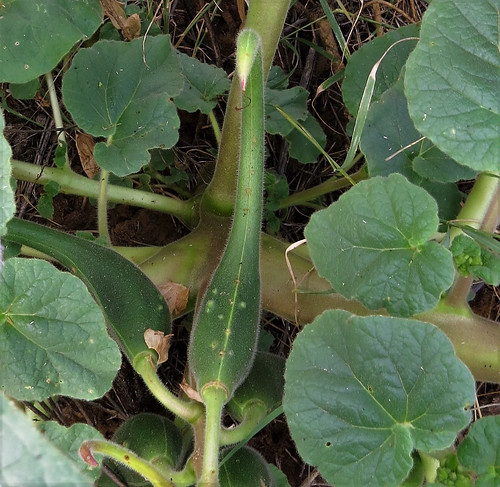
After the flower petals drop away the fuzzy seedhead is revealed.
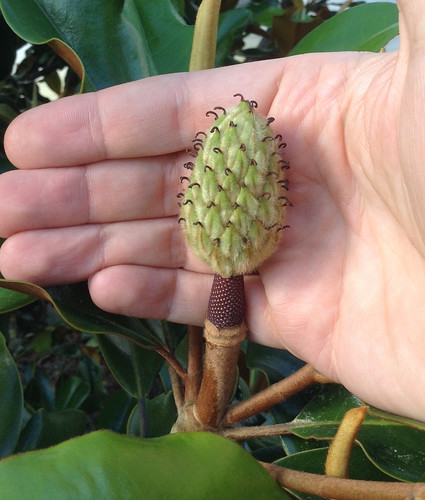

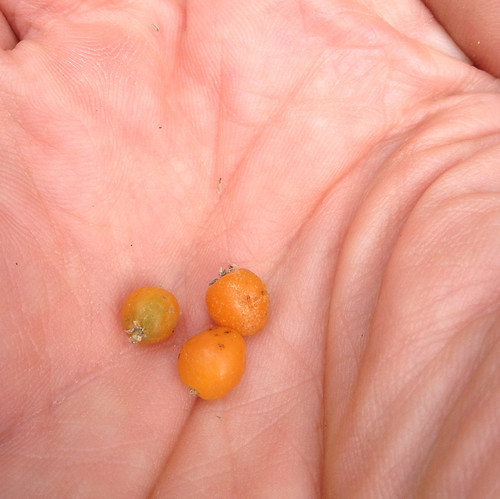
Come fall, the red seeds begin bursting out of the seedhead. The hard, red shell covers a light-tan interior.

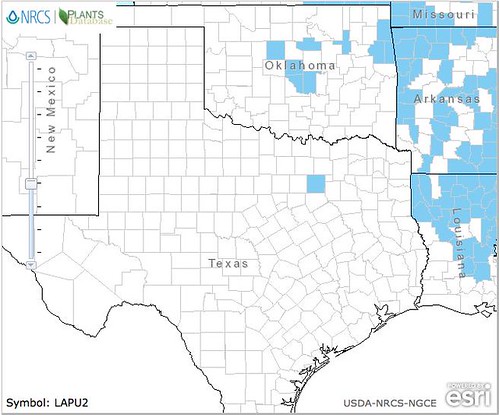
Texas distribution, attributed to U. S. Department of Agriculture. The marked counties are guidelines only. Plants may appear in other counties, especially if used in landscaping.
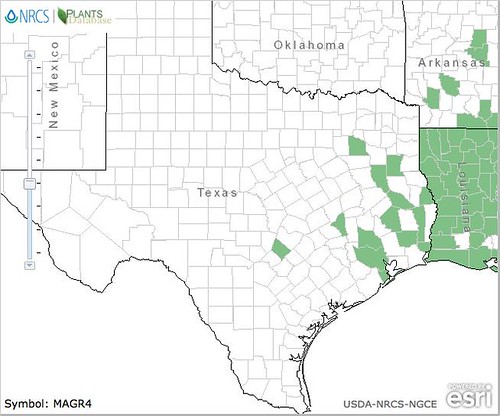
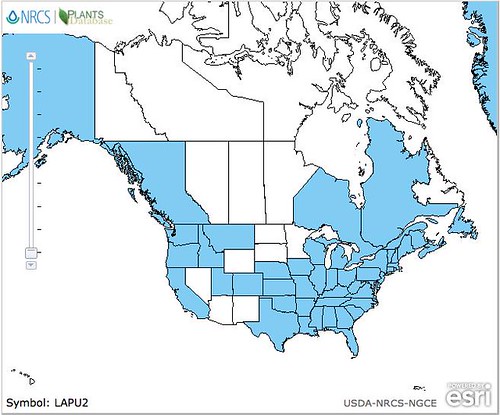
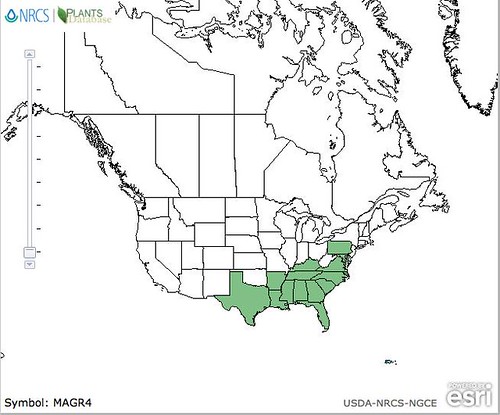
North American distribution, attributed to U. S. Department of Agriculture.
Fifty million years ago Magnolia trees dominated the Earth. Today they are found in the southeastern United States and running down into Central and South America. Oh, how the might have fallen! Yet, there's some pleasure in knowing Texas has some of the last northern holdouts of this ancient race. Looking at these trees, with their giant, ambrosial-scented flowers and thick, leathery leaves, it's not surprising they come from the time of Eocene period, when global temperatures were much hotter than today and plant life thrived.
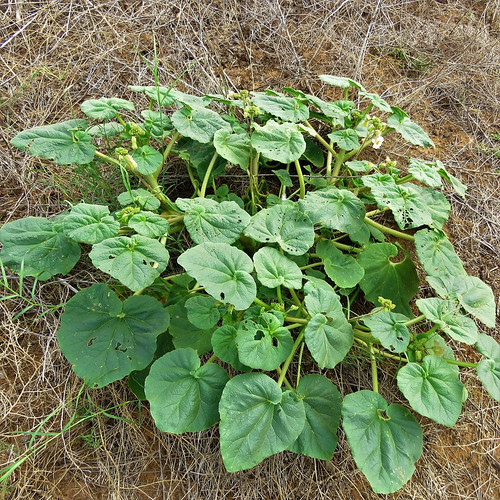
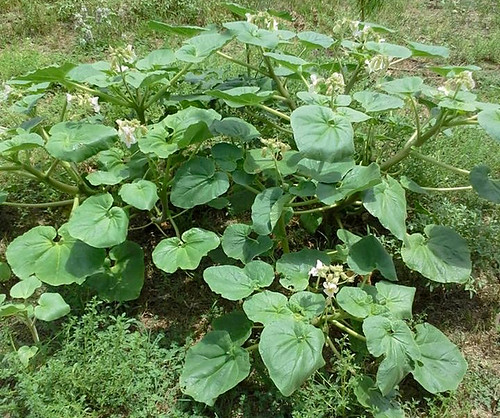
Look for these trees both as landscaping centerpieces as well as wild in the east Texas woods. They keep their large, somewhat oval leaves all year around. Flowers appear in mid-spring followed by the clusters of hard, red seeds in the fall. The bark is relatively smooth and gray with assorted discolorations of lichen. Mature trees can have round crowns forty feet across.
The strong scent of freshly-opened magnolia flowers can be overpowering and so the flowers themselves aren't eaten raw. Shredding the flowers then pickling using the pickled okra recipe in the Ball Complete Book of Home Preserving, produces something similar to pickled seaweed served at sushi joints. A number of bartenders and distilleries have been experimenting with magnolia flower infused gins to create Texas-specific cocktails.
The leaves, after drying, has a long history of herbal medicinal use to fight cancers. Testing by western science has revealed magnolia leaves contain several compounds that reduce the growth of blood vessels to tumors. Lots of work still remains in turning these into an accurate, predictable medicine.
In the fall the trees are covered with clusters of bright red seeds about the size of small jelly beans. Digging through the research on the edibility of these magnolia beans, one find them listed as both poisonous and edible.Being a scientist, I've eaten three of them so far. At the first bite they have a sweet, pleasant flavor but at the second bite my mouth tasted like it was flooded with gasoline. Bleeech! The seeds have the outer, red coat surrounding pale, tan nutmeat. I suspect that the sweet flavor comes from the coat and the gasoline flavor from the nutmeat or perhaps vice-versa. More experimentation with these beans is required.
50 Million year old! Fights cancers! Link leads to another website.