Abundance: uncommon
What: green (unripe) fruit
How: raw
Where: woods, borders, stream banks
When: spring, summer, fall
Nutritional Value: carbohydrates and protein
Dangers: The seeds/fruit contain a POWERFUL laxative when ripe, so avoid purple or black fruit, only eat light-green ones.
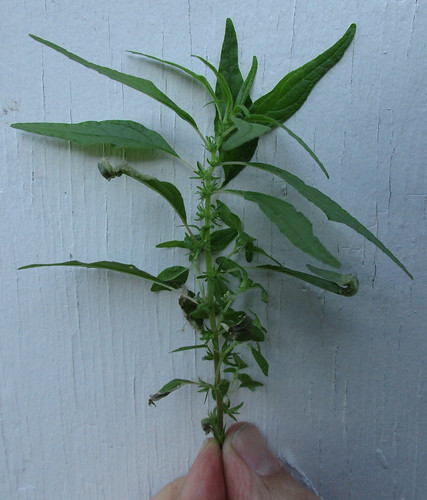
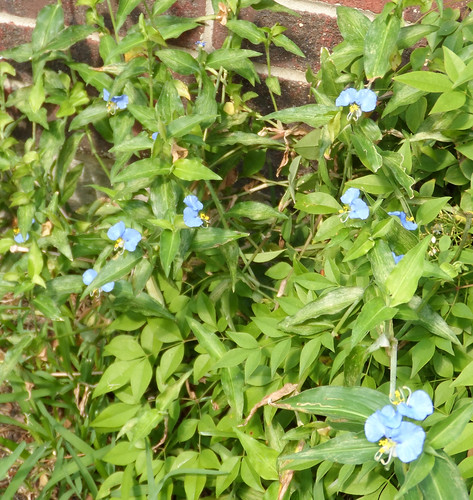
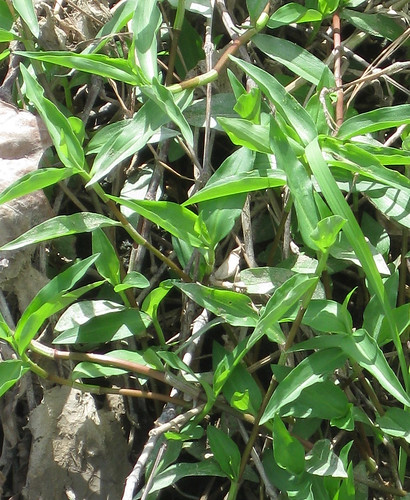
Creeping Cucumber vine with unripe but edible fruit.

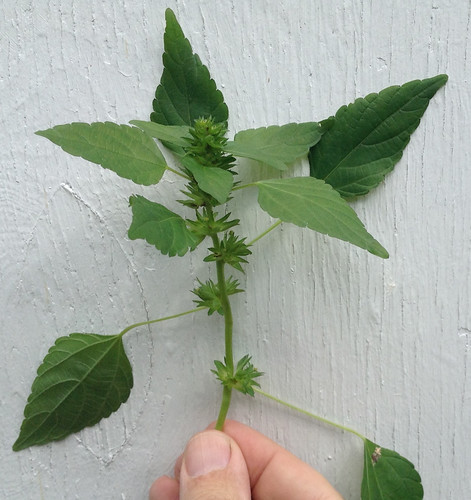
Unripe fruit (which is when you eat it), flower, tendril, and leaf.

The leaf is at a bad angle so you can't see it's true shape.
Close-up of Creeping Cucumber fruit at the right stage to eat.

Fruit cut in half.

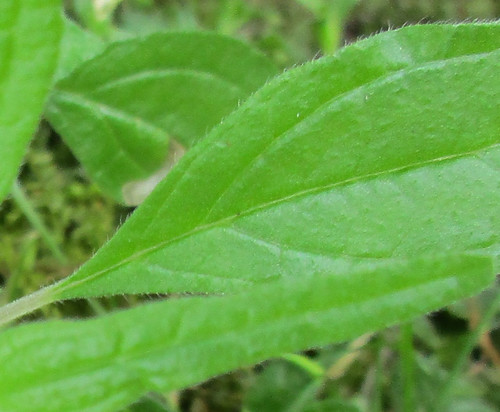
Creeping Cucumber leaf.

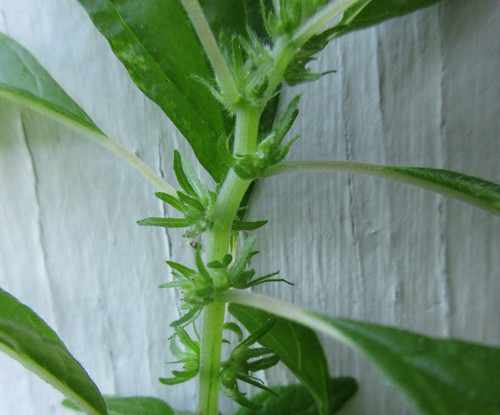
Close-ups of the Creeping Cucumber flower.

Five petals fused at the bases, with a notch in the top of each.

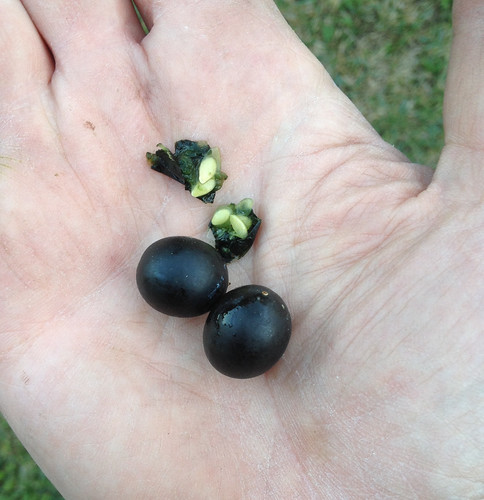
Ripe, purple Creeping Cucumbers, which should not be eaten!

Picture courtesy of Wildcat.
Busted open, the insides of ripe Creeping Cucumbers seem grape-like but with flat, pale seeds.

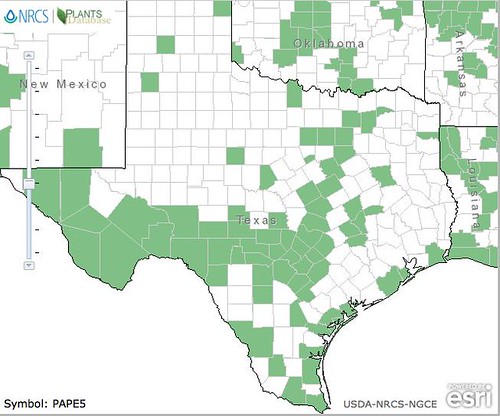
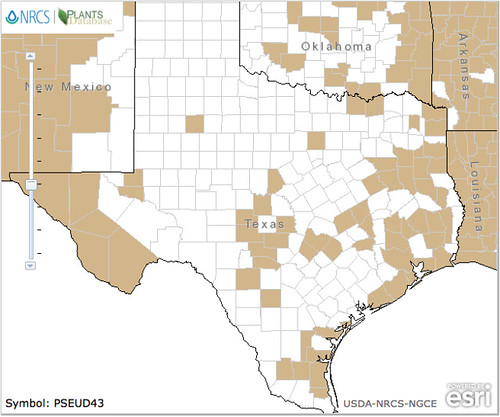
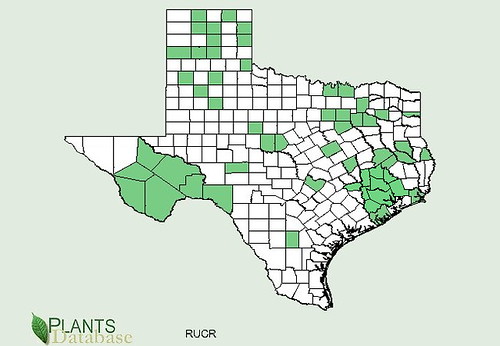
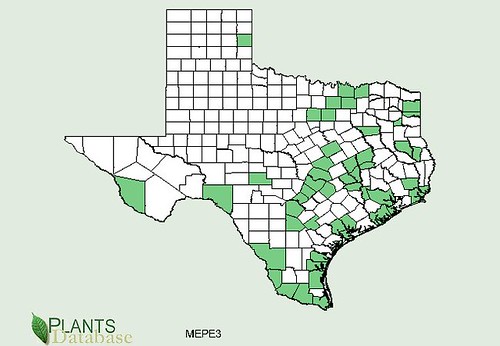
Texas distribution, attributed to U. S. Department of Agriculture. The marked counties are guidelines only. Plants may appear in other counties, especially if used in landscaping.
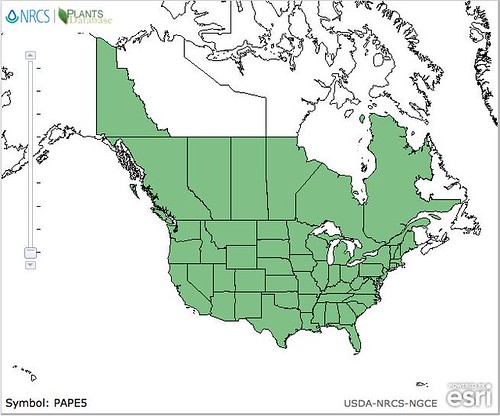
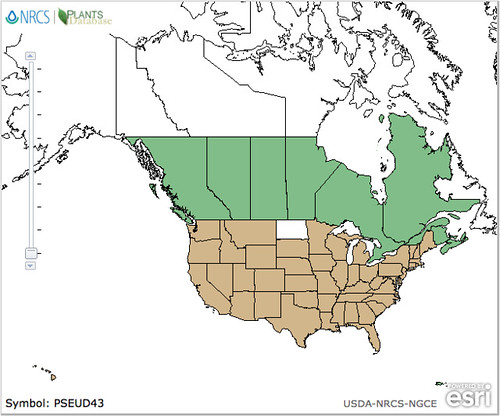
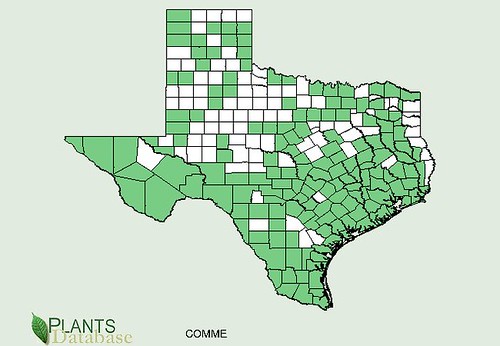
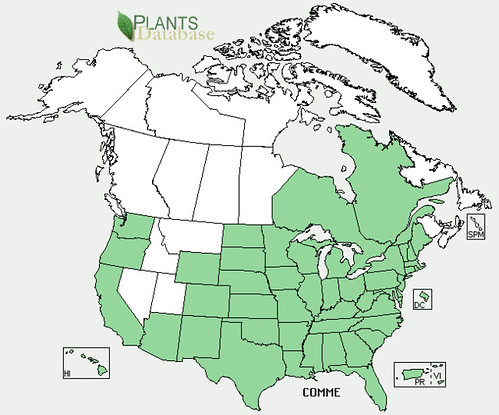
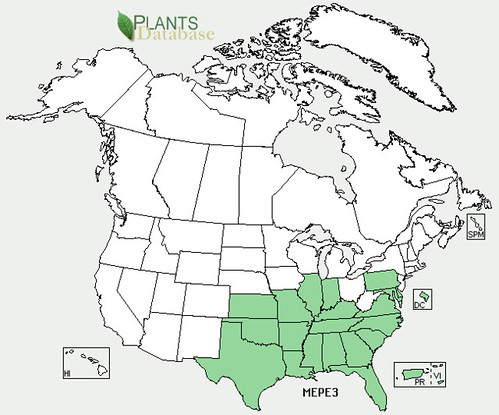
North American distribution, attributed to U. S. Department of Agriculture.
Creeping Cucumbers are tiny, delicious, cucumber-flavored fruit that look like little watermelons when young but then turn a dark purple/black when ripe. Do NOT eat the ripe (purple/black) fruit! At that stage they are an incredibly powerful laxative. Only eat the light-green, watermelony looking fruits.
These vines are found in moist areas both in sun and in shady areas. I've found them along stream banks in the deep shade of the Texas Piney Woods as well as growing along a sunny wall in downtown Houston where a sprinkler kept the soil wet. They begin growing in early spring and continue to live through the summer and fall. They can even be found through the winter if it is mild enough, but a frost usually kills them.
The unripe, light-green fruit is eaten raw without peeling and really does taste just like a cucumber. Use it anywhere you would use a cucumber, though I have not tried making pickles out of them. There's no reason pickling them shouldn't work. The vines will produce new fruit as long as it lives so it's quite common to find flowers, unripe fruit and ripe fruit all on the same vine right up until a frost hits.
I am not kidding when I say the ripe (purple/black) fruit is a powerful laxative. Its bowel-purging effects hits very rapidly and very uncontrollably and can result in serious injury to the body from dehydration.
Buy my book! Outdoor Adventure Guides Foraging covers 70 of North America's tastiest and easy to find wild edibles shown with the same big pictures as here on the Foraging Texas website.