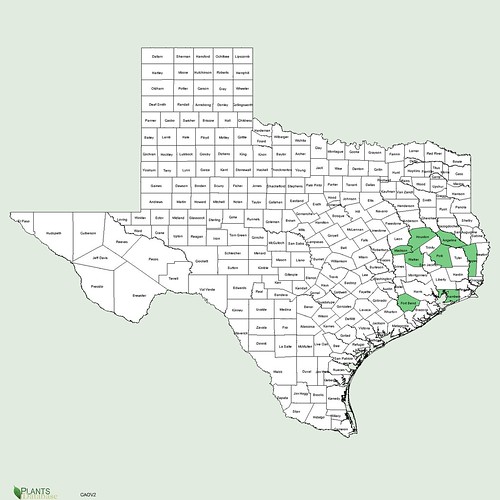
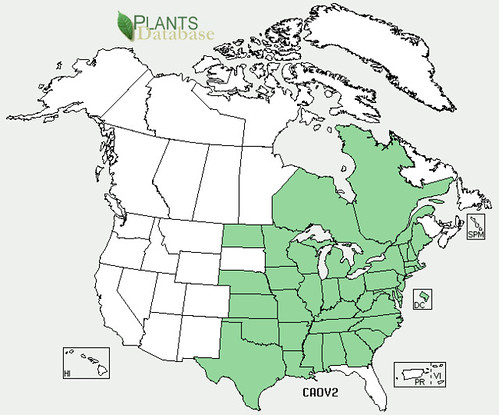
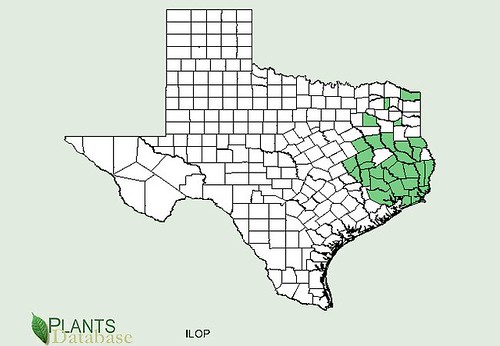
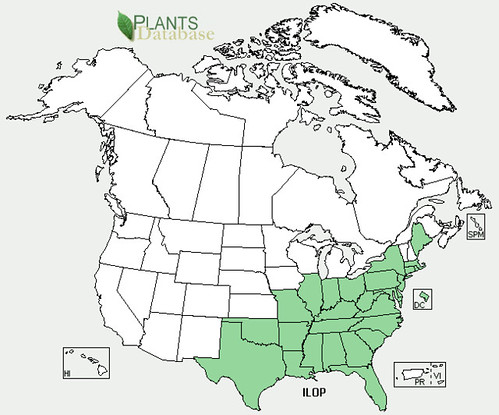
Abundance: rare
What: mushroom
How: cooked
Where: woods
When: fall, winter, spring
Nutritional Value: beneficial compounds
COLLECTING MUSHROOM REQUIRES 100% CERTAINTY. WWW.FORAGINGTEXAS.COM ACCEPTS NO RESPONSIBILITY FOR IDENTIFICATION ERRORS BY ANY READERS.
Lion's Mane (Hericium erinaceus) form "snowball" shapes with spore tubes over 1cm long. Pick when white, not yellow/brown.
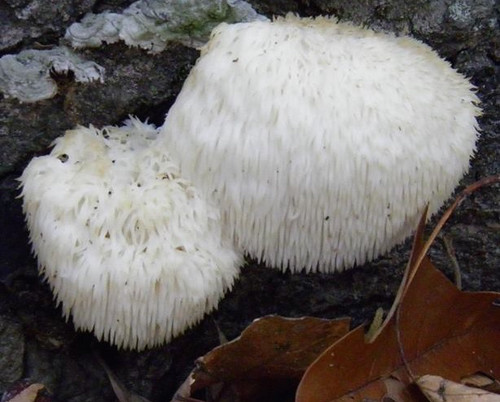
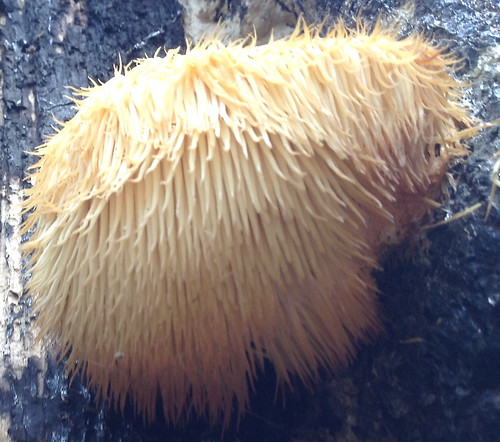



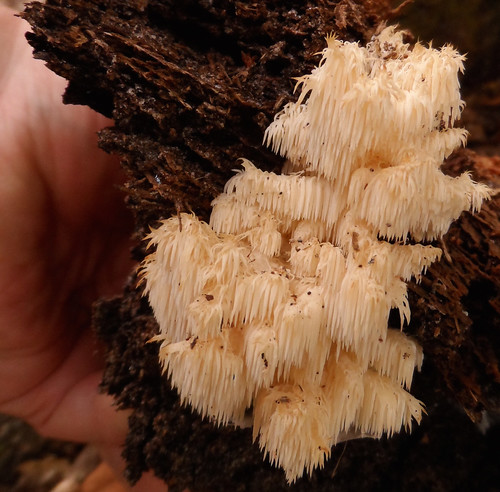
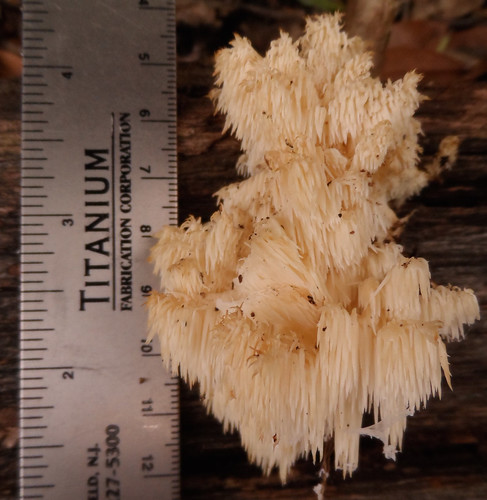
Bearded Tooth (Hericium americanum) form long-toothed "waterfalls".


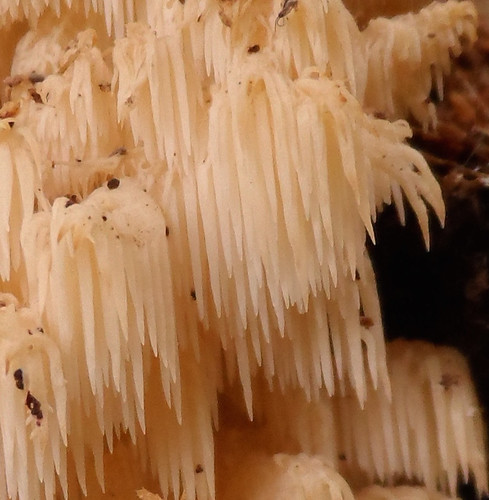
Close-up of Hericium americanum spore tubes.

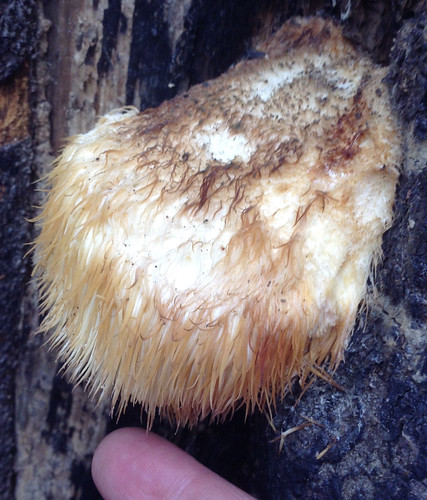
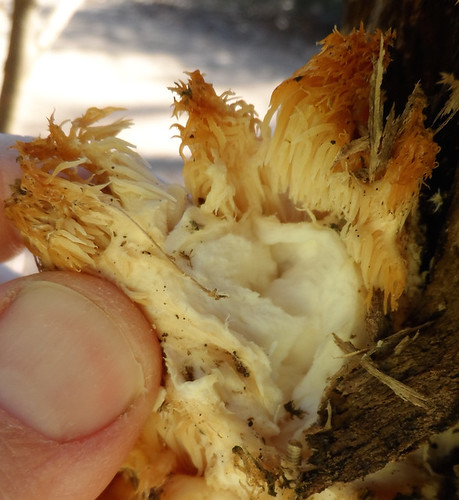
Past-ripe Hericium americanum turn brown but the inner white parts are still edible.

Bear's Head Tooth (Hericium coralloides) grow like H. americium but with shorter spore tubes.
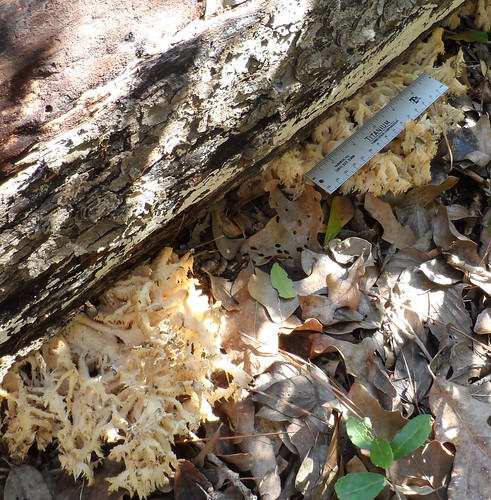
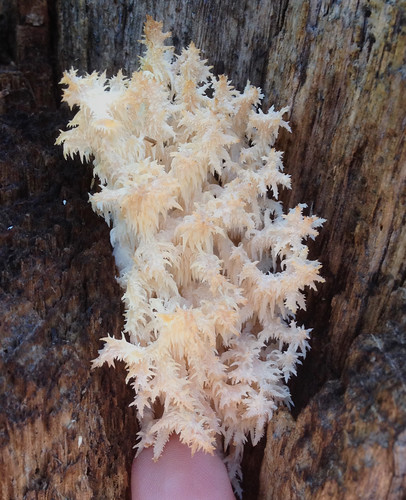
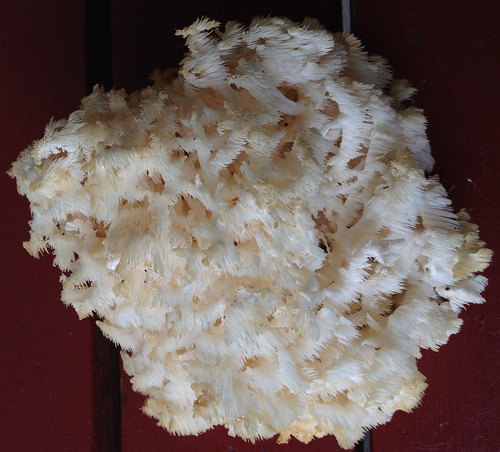
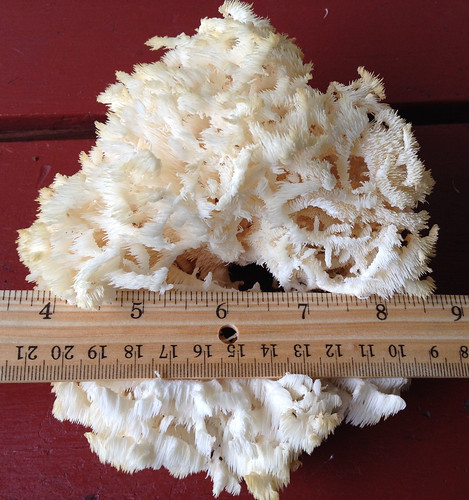




Walking through hardwood forests on a cool day after rains you see an odd sight...a furry looking snowball stuck to a dead tree...or maybe something that looks like coral but far from the sea. A closer examination reveals it is a Hericium mushroom, distinctively made of a cluster of spore tubes and lacking any noticeable cap. They only grow on dead or dying wood so if one of these delicious mushrooms appears on a tree in your yard, be warned.
You want to collect these while they are white or at most slightly off-white. As they mature to a yellow/brown color they are no longer worth eating. These mushrooms must be cooked, with my favorite methods simply cutting them up into 1" pieces then sautéing them in butter until they become just a little crispy at the edges. Once cooked, their flavor is reminiscent of lobster.
Hericium mushrooms are known to contain several compounds that have been found to help with cognitive functions such as memory/recall as well as mood issues such as depression and anxiety. There's also some evidence that they reduce the plaque in the brains of Alzheimer’s patients. This is an amazing family of mushrooms!
Buy my book! Outdoor Adventure Guides Foraging covers 70 of North America's tastiest and easy to find wild edibles shown with the same big pictures as here on the Foraging Texas website.