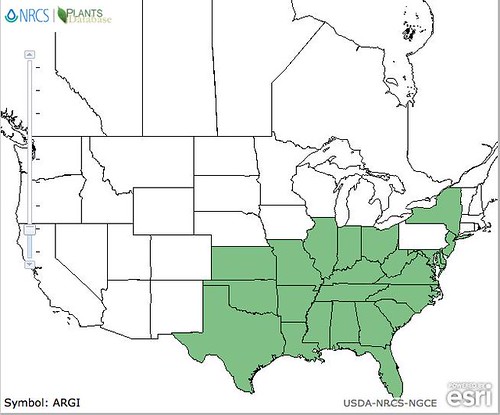
Scientific name: Tilia americana
Abundance: rare
What: flowers, leaves, buds, inner bark
How: leaves raw in salad, buds to nibble, flowers for tea, cambium (inner bark) raw or boiled for calories
Where: Sunny edges of woods
When: buds in late winter, young leaves spring/summer, flowers summer, cambium all year
Nutritional Value: Leaves contain vitamins and minerals, inner bark has carbohydrates
Other uses: cordage from bark, not a good firewood
Leaf Arrangement: Basswood trees typically have alternate leaf arrangement along the branches.
Leaf Shape: Leaves are generally large, heart-shaped, with lengths ranging from 4 to 6 inches.
Leaf Venation: Prominent veins are visible on the leaves, contributing to their overall structure.
Stem Characteristics: The stems are usually slender, and the trunk can reach diameters of 2 to 4 feet.
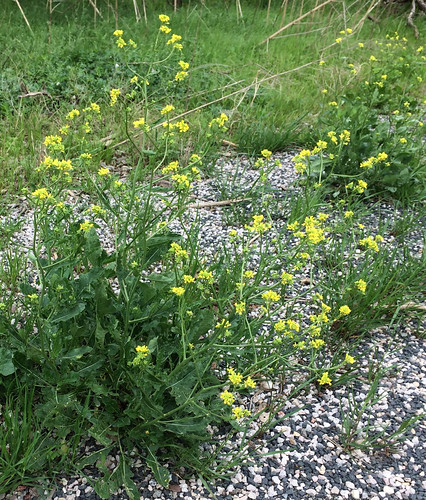
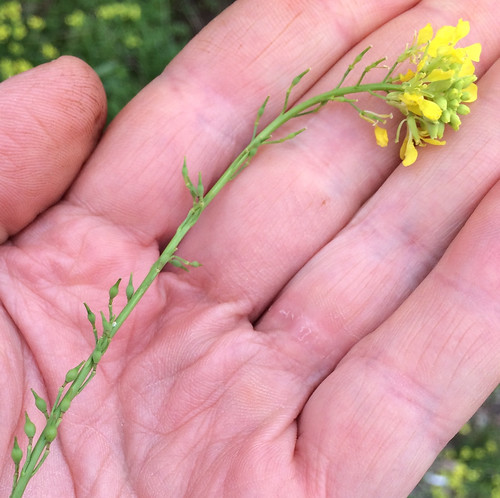
Flower Cluster: Basswood trees produce fragrant, pendulous clusters of small, pale-yellow to cream-colored flowers in late spring or early summer.
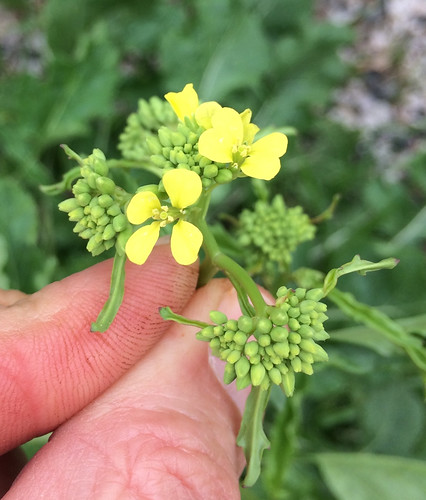
Flower Structure: Individual flowers are small and have five petals. Flowers can be around 0.2 to 0.3 inches in size.
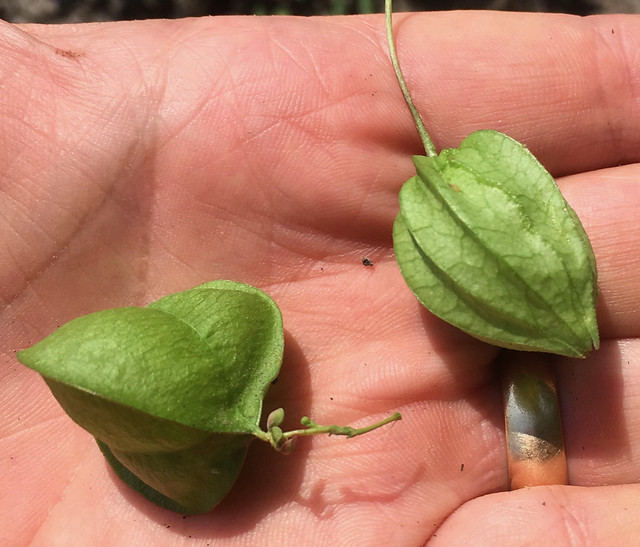
Seed: The seed is enclosed in a papery wing, forming a structure known as a samara. The wings can measure around 1 to 2 inches in length, looking like a leaf. A several seed capsule pairs, all branching from a single stem, dangle down from the leaf-like wing.
Seed Characteristics: Seeds are small and brown, typically located at the center of the samara.
Height: Basswood trees can reach heights of 60 to 80 feet, with variations based on age and growing conditions.
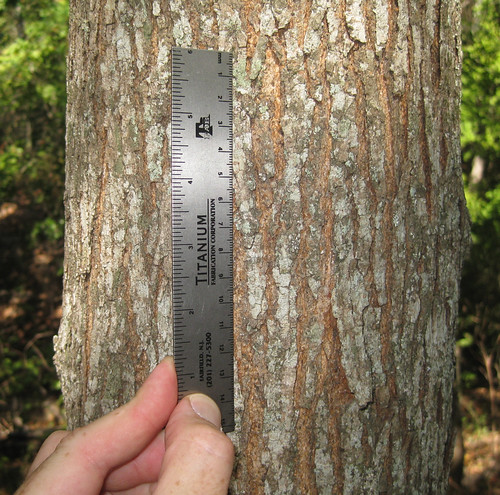
Bark: The bark of young trees is smooth and light gray, becoming more furrowed and darker with age. Bark color can range from light gray to dark gray-brown.
Hairs: Young shoots and leaves may have fine hairs, but mature leaves are generally smooth. Inspect young shoots and leaf undersides for pubescence.
Fruit: The fruit consists of the winged samaras, which are produced in clusters as described above, and become tan to light brown as they mature.
Basswood tree used in urban landscaping.

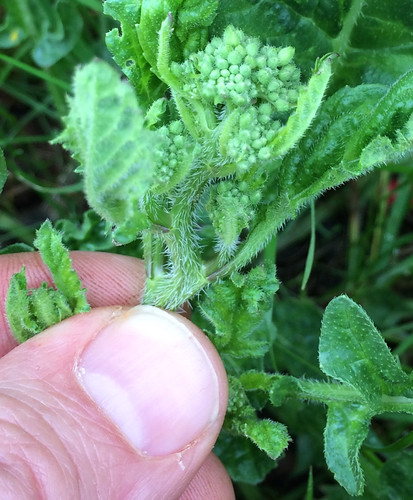
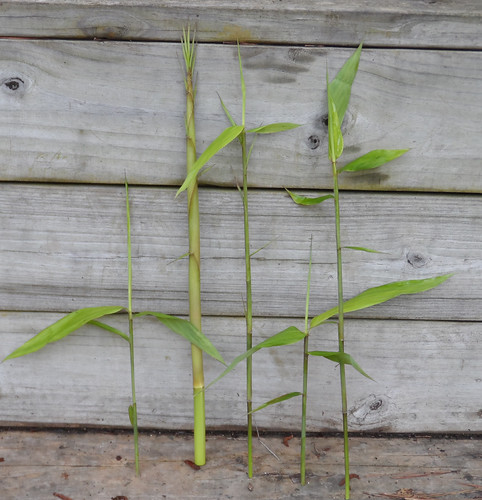
Basswood leaf and flower/nut bract (long, narrow leaf-like thing).

Basswood flower cluster and flower bract.

Close-up of Basswood flowers.

Basswood leaves and seedpods.



Basswood leaves.

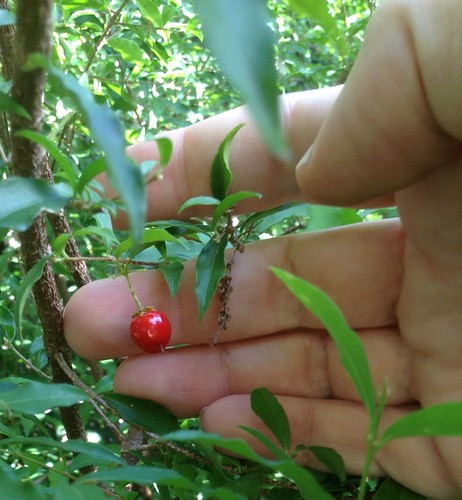
Almost-ripe Basswood nuts in the fall.

Ripe Basswood nuts.

Basswood bark.

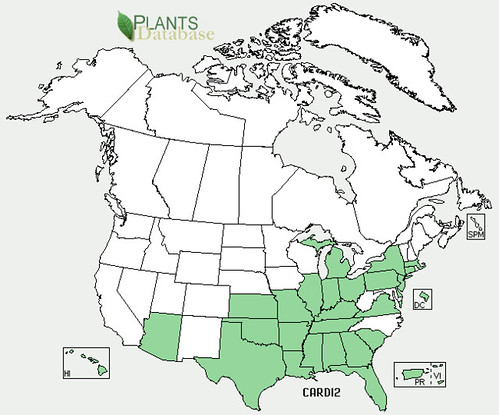
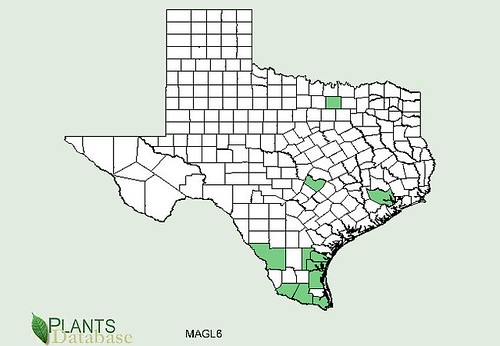
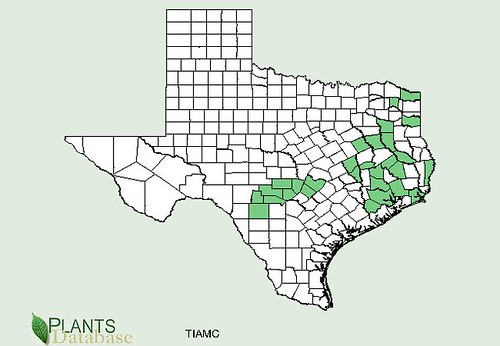
Texas distribution, attributed to U. S. Department of Agriculture. The marked counties are guidelines only. Plants may appear in other counties, especially if used in landscaping.
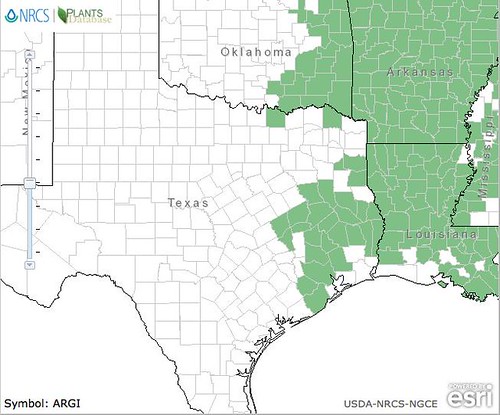
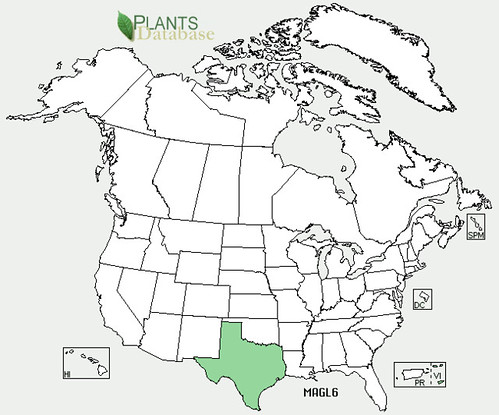
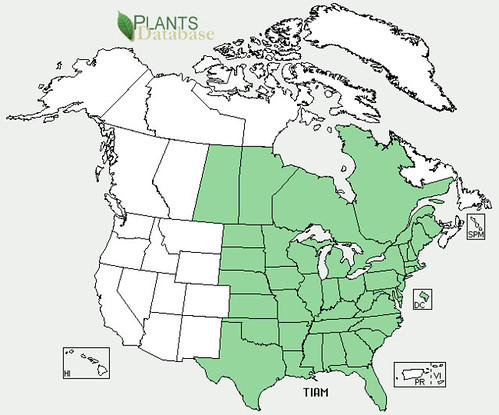
North American distribution, attributed to U. S. Department of Agriculture.
Stately basswood trees range from 60 to 120 feet tall with shallowly-furrowed, somewhat greyish bark and round crowns. There are thirty species in North America with Tilia Americana and Tilia caroliniana being the most common in Texas. Basswoods prefer loose, well-drained soil with access to moisture, in particular river flood-plains and in low areas of woods.
The sweet sap, running in the spring before the leaf buds open, can be boiled down into a syrup or just drank as-is. Be sure to sterilize your tools before using them to cut or drill into the tree to collect sap or inner bark. This reduces the chance of a fungal infection striking the basswood.
A very delicious, spicy tea is made from the small flowers of basswood trees, which appear in the spring. The flowers can also be eaten raw. Bees love these flowers and often the tree can be found just by listening for the buzz of the hundreds of bees collecting its nectar. The resulting honey has a flavor imparted from the basswood nectar.
The young leaf buds and leaves can be eaten raw and have a slightly sweet flavor similar to the flowers. These parts can also be cooked like pot-herbs.
In the fall the nuts make a good trailside nibble while hiking, but only eat the inner meat, not the nuts’ outer shells.
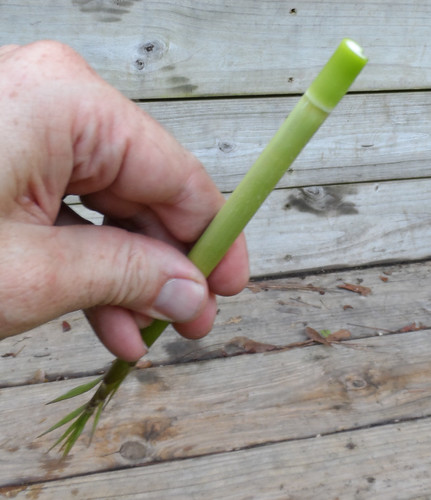
The calorie-rich cambium layer, just under the bark, is stripped, finely diced, and boiled into a porridge-like mush to eat any time of the year. In Europe towards the end of World War II basswood sawdust was added to bread to try and produce enough loaves to fill everyone’s belly.
This cambium layer can be used to make strong fibers that can be woven into rope, containers and crude cloth. This inner bark must be soaked for up to two weeks to rot away the majority of the plant’s cells, leaving behind just the fibers. The wood itself is great for carving and for making the body of guitars.
Buy my book! Idiots Guide Foraging covers 70 of North America's tastiest and easy to find wild edibles shown with the same big pictures as here on the Foraging Texas website.
Buy my book! Outdoor Adventure Guides Foraging covers 70 of North America's tastiest and easy to find wild edibles shown with the same big pictures as here on the Foraging Texas website.