Abundance: plentiful
What: flowers, leaves, stem
How: flowers raw or cooked, leaves salad, stem steamed or cooked
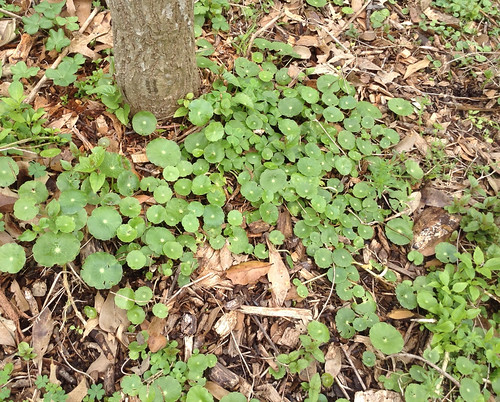
Where: shade, partial sun, woods, fields, landscaping
When: spring, late summer, fall
Nutritional Value: minor amounts of vitamins and minerals
Other uses: the normally blue stamen hairs indicated mutation by turning pink when exposed to radiation. The same effect has since been observed when the spiderwort plant is subjected to chemical pollution.
Dayflower plants in the morning.
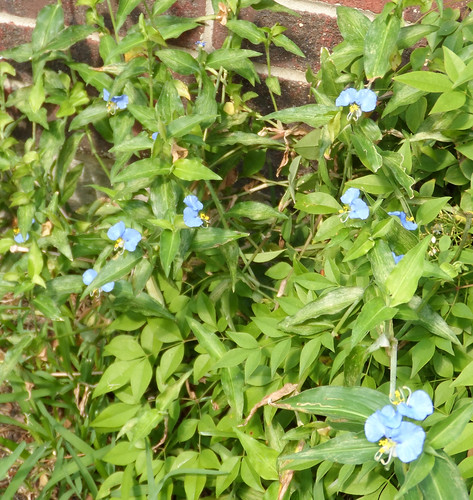

Dayflower plants in the afternoon after the day's flowers have gone away.
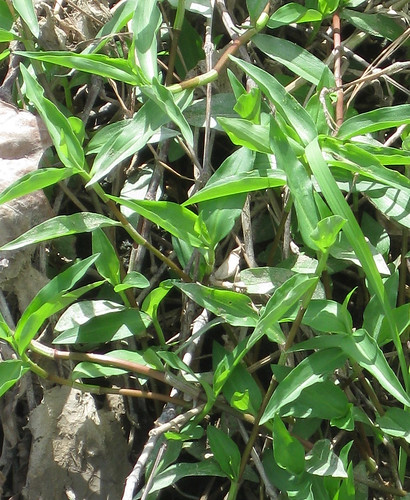

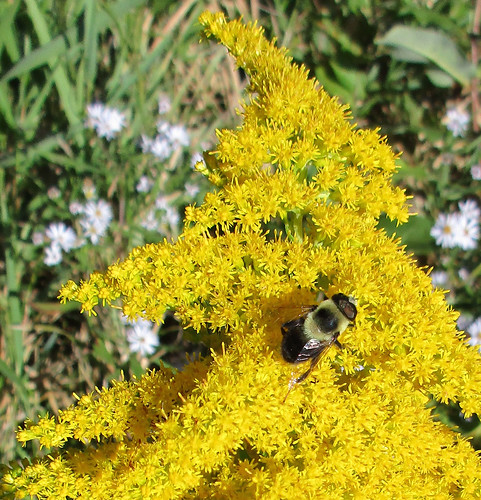
Close-up of dayflowers.

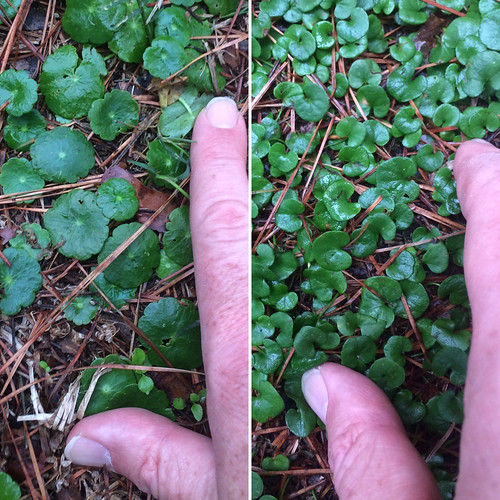
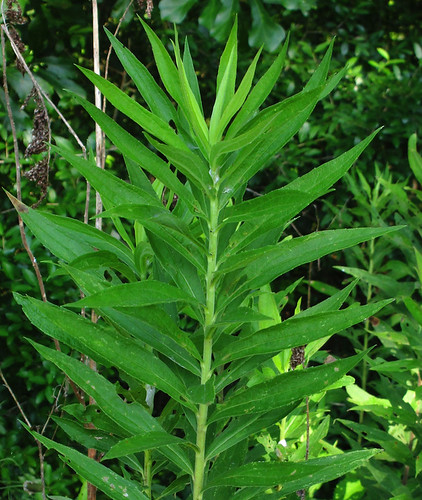
Close-up showing a leaf, too.

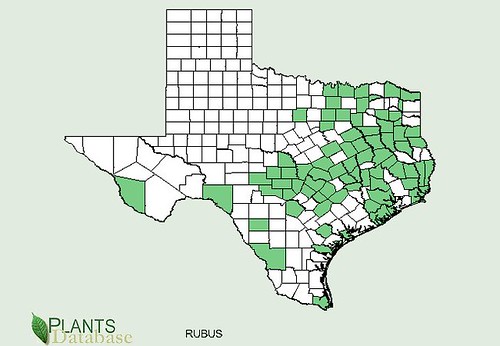
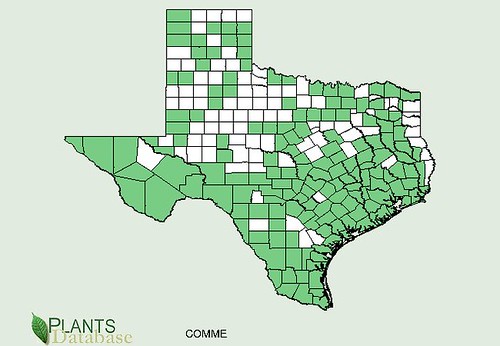
Texas distribution, attributed to U. S. Department of Agriculture. The marked counties are guidelines only. Plants may appear in other counties, especially if used in landscaping.
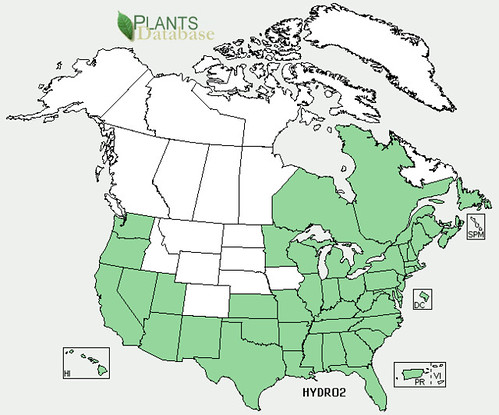
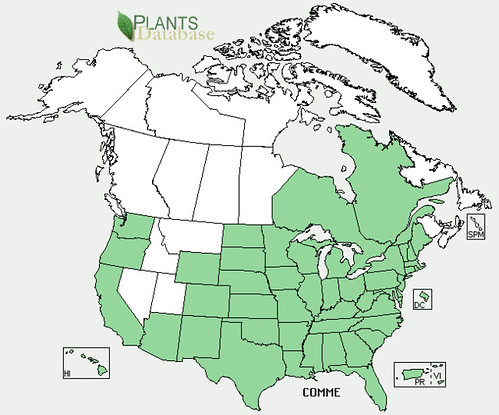
North American distribution, attributed to U. S. Department of Agriculture.
In just about everyone's flowerbed creeps Dayflower. The thin, weak stems fall over until there's so many present that they force each other upright. In the morning these stems will end in blue, two-petal flowers coming out of a green, beak-like structure. The flowers don't last though, shriveling up a little after the solar noon. The tough leaves have a a parallel vein structure and join to the stem with a sheath which runs down the stem approximately 1/4 inch. This plentiful weed appears in the spring and grows through the summer and fall, dying back only when a hard frost hits it. Be warned, if you just pull it up from your garden or flowerbed and toss it aside it'll take root and begin growing wherever it lands and touches soil.
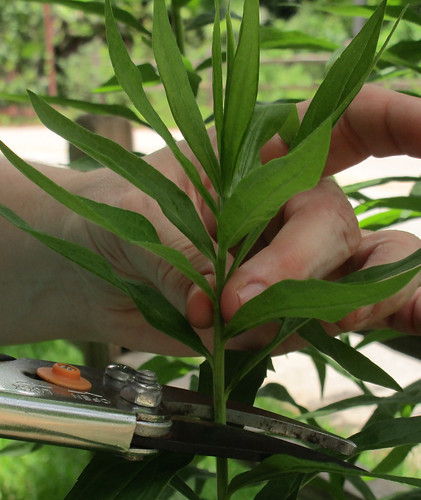
Dayflowers are slightly more tender than Spiderworts, but are still tough. Because of this, even though the entire plant is edible I rarely use any more than just the top cluster of flowers and flower buds. These bits can be added to salads for a splash of color or tossed into cooked dishes, too. On rare occasions I'll include the uppermost 1-3 leaves if I'm making a curry or stew that'll be simmered a long time. While the stems do contain a slime, the quantity is too low to be a worthwhile thickening agent or first aid gel.
Buy my book! Outdoor Adventure Guides Foraging covers 70 of North America's tastiest and easy to find wild edibles shown with the same big pictures as here on the Foraging Texas website.