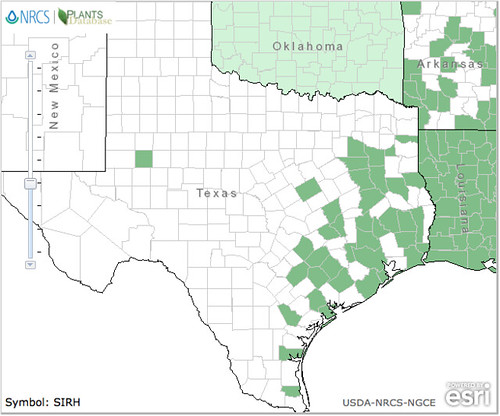
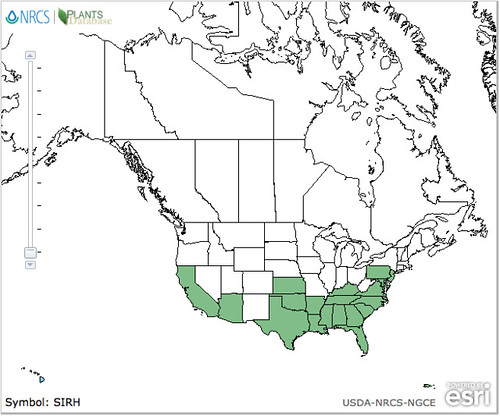
Scientific Name(s): Cantharellus cinnabarinus, Cantharellus texensis, Cantharellus lateritius, Cantharellus cibarius
Abundance: uncommon
What: above ground caps and stems
How: cooked
Where: woodlands, near oaks; some yards
When: spring, summer
Nutritional Value: minor
Dangers:
COLLECTING MUSHROOM REQUIRES 100% CERTAINTY. WWW.FORAGINGTEXAS.COM ACCEPTS NO RESPONSIBILITY FOR IDENTIFICATION ERRORS BY ANY READERS.
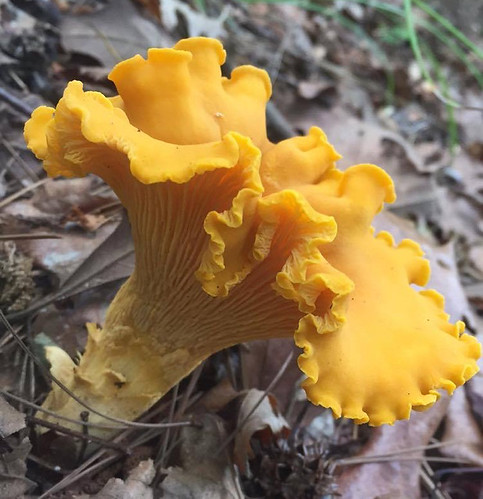
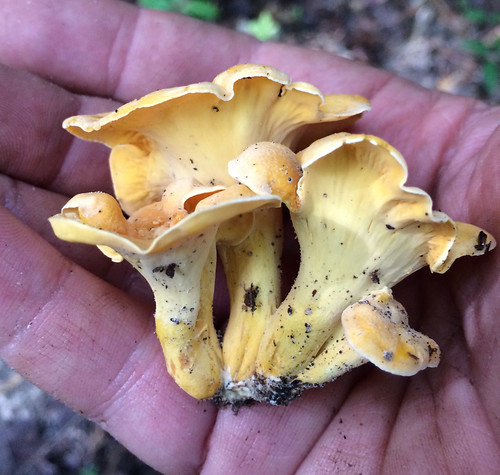
Cantharellus cibarius.
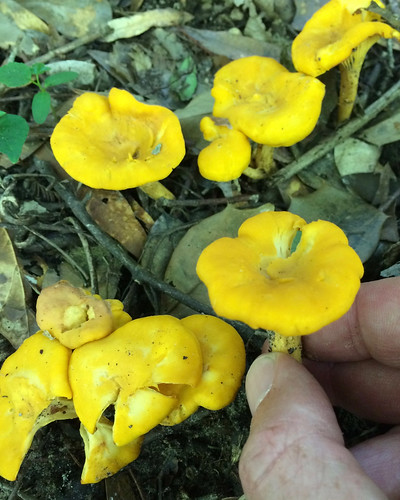
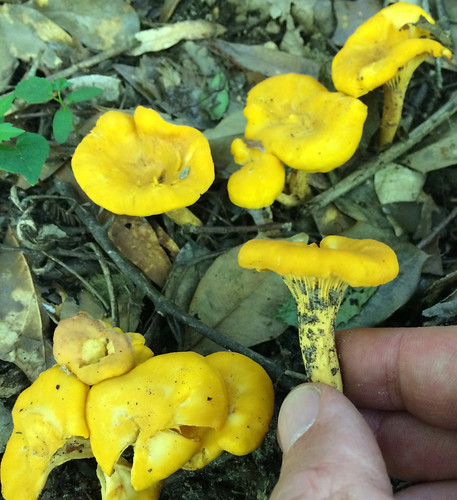


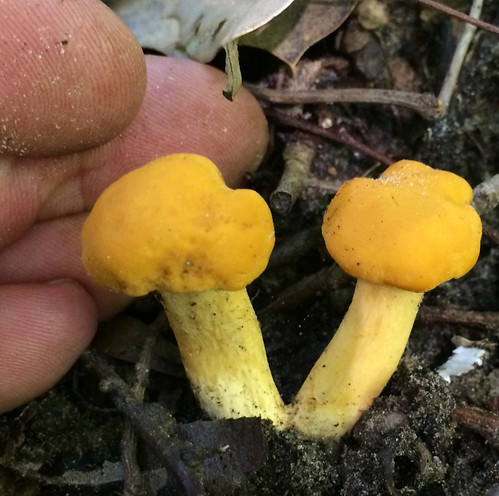
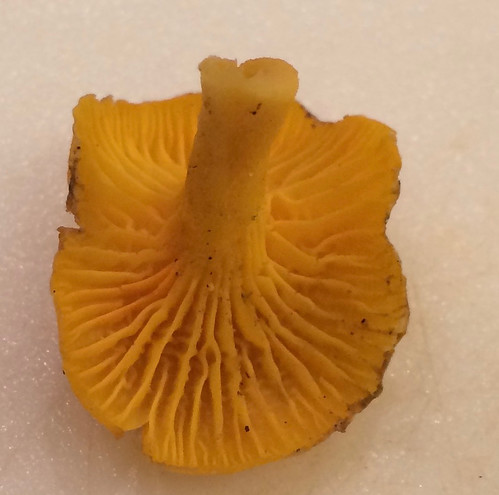
Note how the gills run down into the stem.
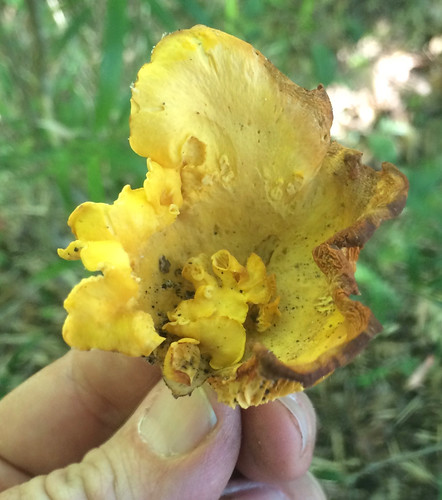
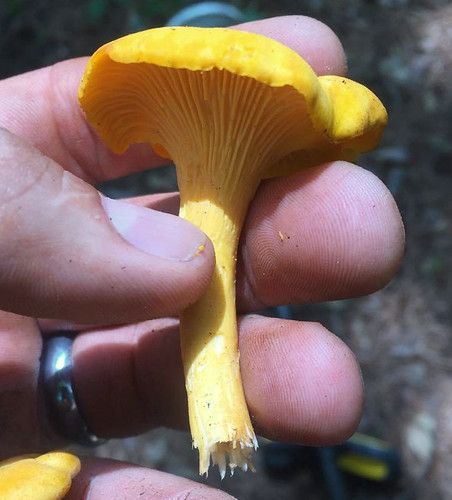
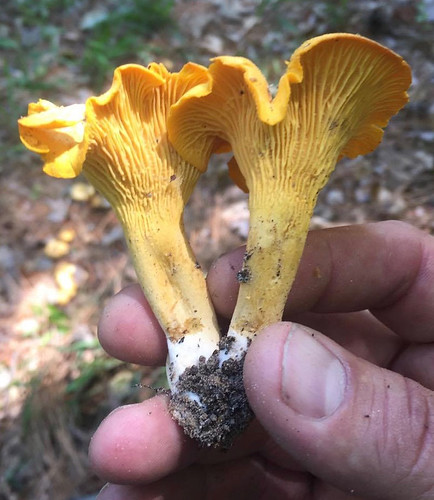








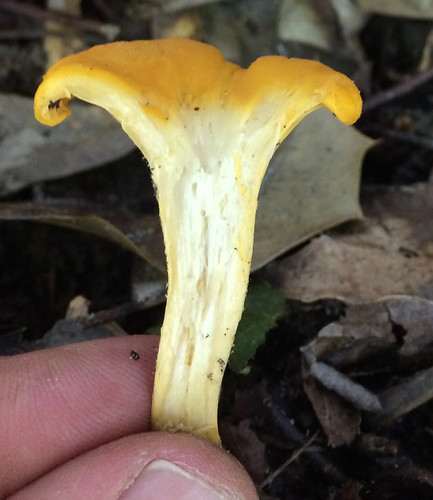
Cross-section showing the false gills. There is no demarcation between the cap and the "gill" structures, they are all one continuous unit.

Cantharellus cibarius Structural Features::
Growth Form: A highly prized, fragrant, edible mushroom, typically found on forest floors in summer and autumn. It has a symbiotic, mutualistic association with tree roots, often found near oak and beech trees.
Cap Shape and Size: Funnel-shaped with a diameter up to 4 inches, featuring a wavy, irregular margin, and varying from light yellow to deep egg-yolk yellow.
Gills or Pores: The gills are actually ridges that are forked and generally have blunt edges, wavy, and always decurrent.
Stipe Characteristics: The stem is central, fleshy, curved, smooth, and measures 2.4-3 inches long and 0.2-0.4 inches wide.
Odor: Has a somewhat apricot-like scent.
Spore Color: Pale yellow to creamy white, sometimes with a slight pinkish tinge.
Substrate and Habitat: Found in deciduous forest soils near oak, often under beech trees. Grows in many countries including Canada, the U.S., Europe, the Mediterranean, parts of eastern and southern Australia, and parts of Asia.
Other Characteristics: The chanterelle's flesh is thick and firm.
Cantharellus lateritius false gills aren't as produced as those of other chanterelles.
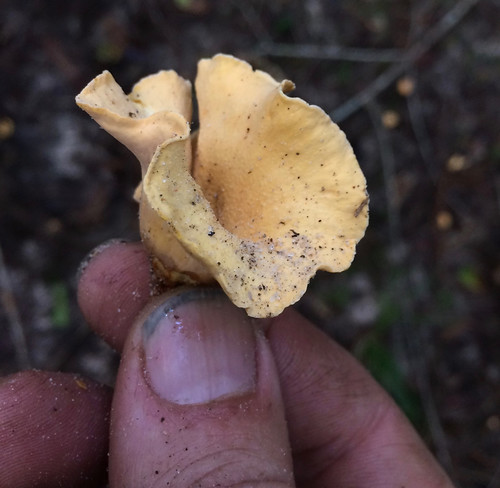






Cantharellus lateritius Structural Features:
Growth Form: Mycorrhizal with oaks and sometimes hickories. Found growing alone, scattered, gregariously, densely gregariously, or in loose clusters during summer and fall. Widely distributed east of the Rocky Mountains.
Cap Shape and Size: 1-3.15 inches across; planoconvex to flat when young, becoming shallowly vase-shaped with an incurved, wavy, and irregular margin. Color ranges from bright orange-yellow to egg-yolk yellow. ally more developed wrinkles near the margin. Colored like the cap but paler, often with a pinkish hue.
Stipe Characteristics: 1-2.5 inches long, 0.5-1.2 inches thick, tapering to the base. The stem is bald, colored like the cap or paler, and bruises slowly yellowish to orangish brown.
Bruising: Bruises slowly yellowish to orangish brown, occasionally blackening at the margin.
Gills or Pores: The undersurface runs down the stem; smooth or with shallow wrinkles, occasionally more developed wrinkles near the margin. Colored like the cap but paler, often with a pinkish hue.
Odor: The taste is not distinctive, but the odor is usually strong, fragrant, and sweet, reminiscent of apricots.
Spore Color: Pale pinkish yellow.
Substrate and Habitat: Found in deciduous forest soils near oak, often under beech trees.
Cantharellus texensis
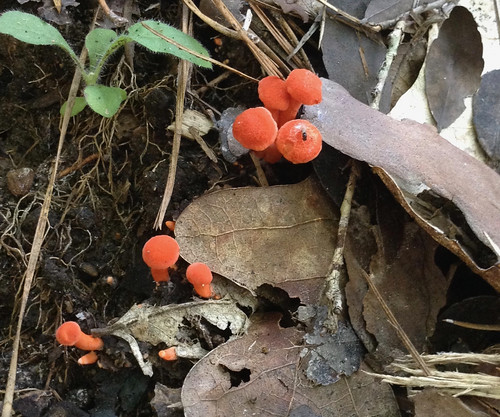
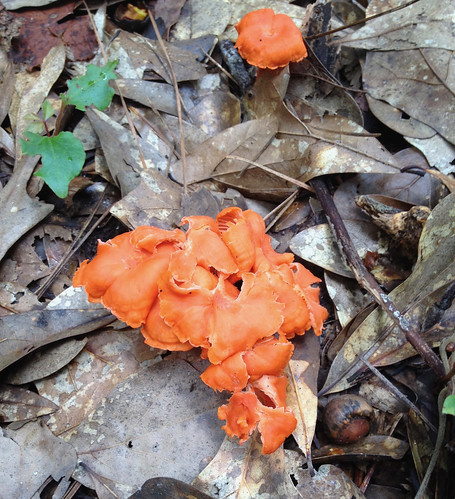
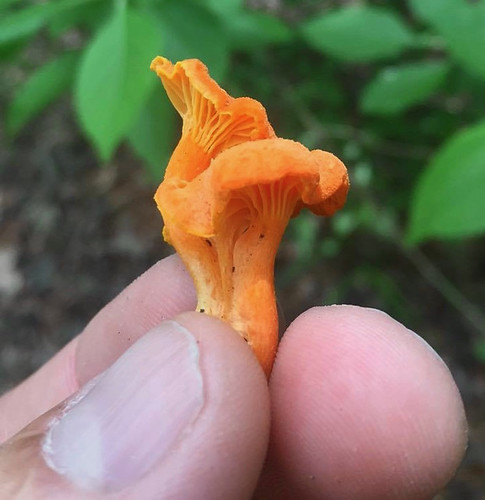
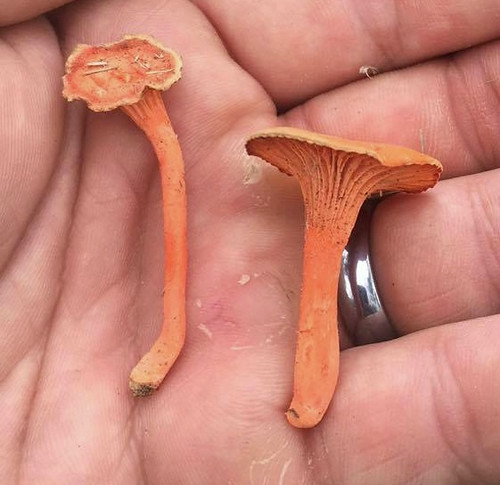





Cantharellus texensis & Cantharellus cinnabarinus Structural Features:
Growth Form: Typically grows in the traditional "toadstool" shape, in a solitary or scattered pattern.
Cap Shape and Size: The cap is funnel-shaped, with a size ranging from 1 to 2.5 inches in diameter. It exhibits a bright orange to cinnabar-red color.
Gills or Pores: This mushroom features false gills that are shallow, well-spaced, and run down (decurrent) the stem. The gills are the same color as the cap.
Stipe Characteristics: The stipe (stem) is 1 to 2.5 inches long and 0.25 to 0.5 inches thick, with a color similar to the cap. It is smooth and solid.
Odor: They have a mild, fruity odor, not easily distinguishable.
Bruising: Bruising is not a significant characteristic for this species; there are no notable changes in color when bruised.
Spore Color: The spores are pale yellow to white in color.
Substrate and Habitat: Like most North Anerican Cantharellus, these are commonly found in hardwood forests, particularly under oaks, in the spring and fall.
Other Characteristics: Notable for its bright color, these mushrooms have a peppery taste.
Walking through the Texas hard wood forests after several days of summer rain, a forager's eye will invariably spot gold and bright red mushrooms growing up from the forest floor, especially along ravines and washes. Most commonly, they will be near oak trees as these fungi treasures have developed a symbiotic relationship trading needed chemicals with the oak roots. They seem to like daytime temperatures between 80F and 100F. I personally use Mother's Day as the signal to start looking and September 1st as the end date.
There are several key physical traits you need to look for on chanterelles to properly identify these awesome, edible mushrooms. That they grow out of the ground in hardwood forests has already been stated. They do NOT grow on living or dead wood. All chanterelles have false gills, meaning their cap and gill structures are one continuous unit. They don't have gills but rather the underside of the cap is very wrinkled to the point of looking like gills. When cut in half it is easy to see there's no change in between the cap and the false gill material. These false gills will run down and merge into the stem, a term described as "decurrent". The stem lacks any ring or bulb at it's base. Several mushrooms may be joined together at the base of their stems. The caps are shaped like an upside down bowl when very young but soon invert into a funnel (convex) shape. Spore prints will be light gray/white in color.
Chanterelles sautéed in butter with a bit of garlic and a splash of homemade wine is very hard to beat. These mushrooms can be used in all the "normal" ways that mushrooms are cooked. The golden chanterelles has a mild, almost fruity flavor while the red cinnabarinus have a spicy, peppery flavor. They dry well for longterm storage and are usually rehydrated in hot water before use.
There are two poisonous mushrooms in my opinion that a novice might mistake for chanterelles. These poisonous mushrooms are Sulfur Tufts (Hypholoma fasciculare) and Jack O'Lanterns (Omphalotus illudens). Let's look at those, starting with the Sulfur Tuft mushroom.
Sulfur Tufts (POISONOUS!) going off buried pine root.
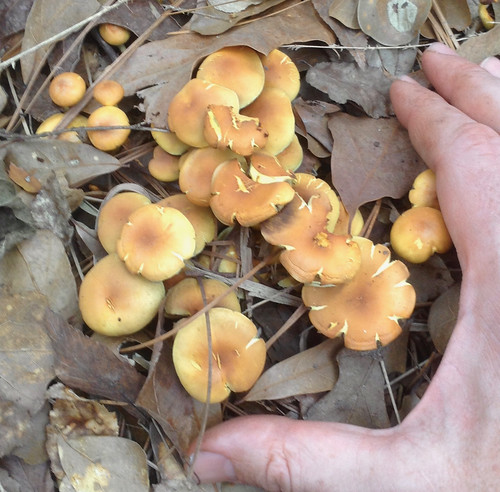
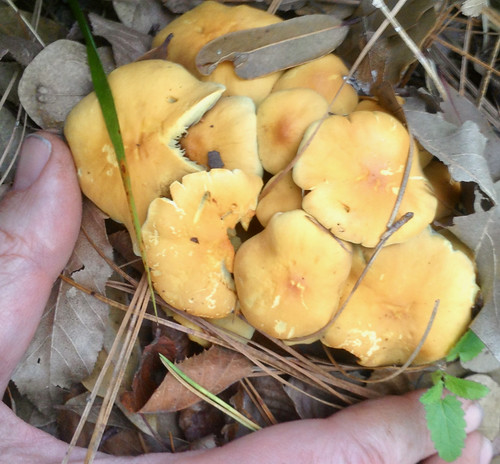


Unlike chanterelles, sulfur tufts grow on the dead wood of pines. Their caps will look similar to chanterelle but sulfur tufts have true gills and these gills may start yellowish but turn greenish then darken greatly as spore production gets heavy. The gills come to a sharp stop at the stem. Spore prints will be purple-brown.
Jack O'Lantern (POISONOUS!)
Like the sulfur tufts and again unlike chanterelles, Jack O'lanterns grow on dead/dying hardwood. They are dark orange in color, and have true gills which end at the stem. Jack o'lantern spore prints will be pale, creamy, or yellowish.

By Antonio Abbatiello [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons
Buy my book! Outdoor Adventure Guides Foraging covers 70 of North America's tastiest and easy to find wild edibles shown with the same big pictures as here on the Foraging Texas website.